15 - The Periphery
ucla | GEOG 4 | 2023-11-27 03:01
Table of Contents
Background
- what is happening in the world beyond the core
Colonialism and modern world economy
Background
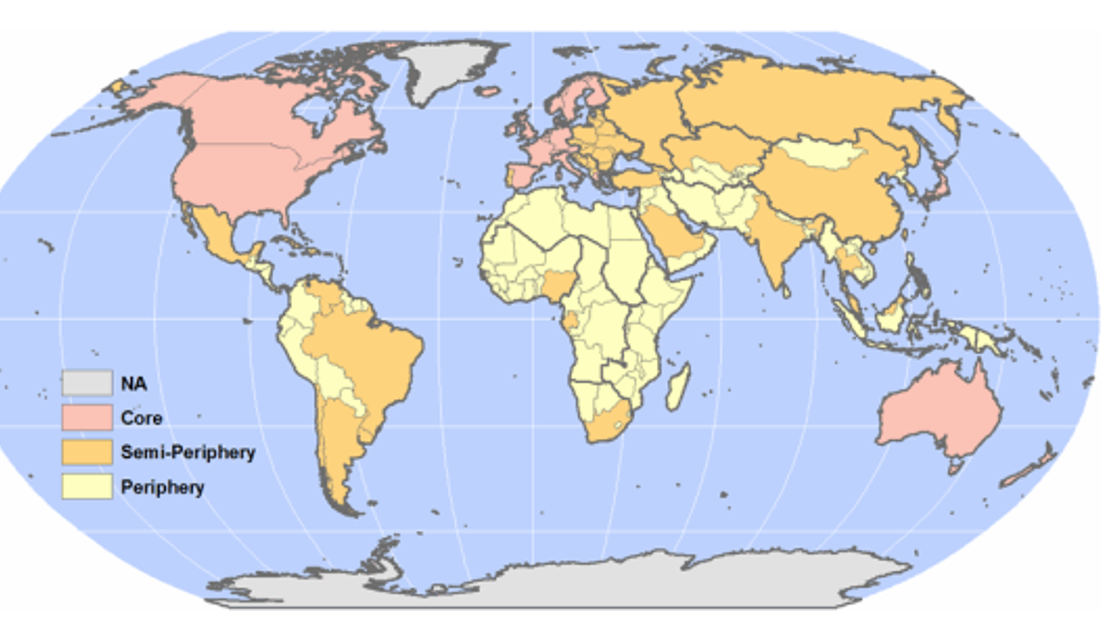
- 3 zones: core, periphery, semi-periphery
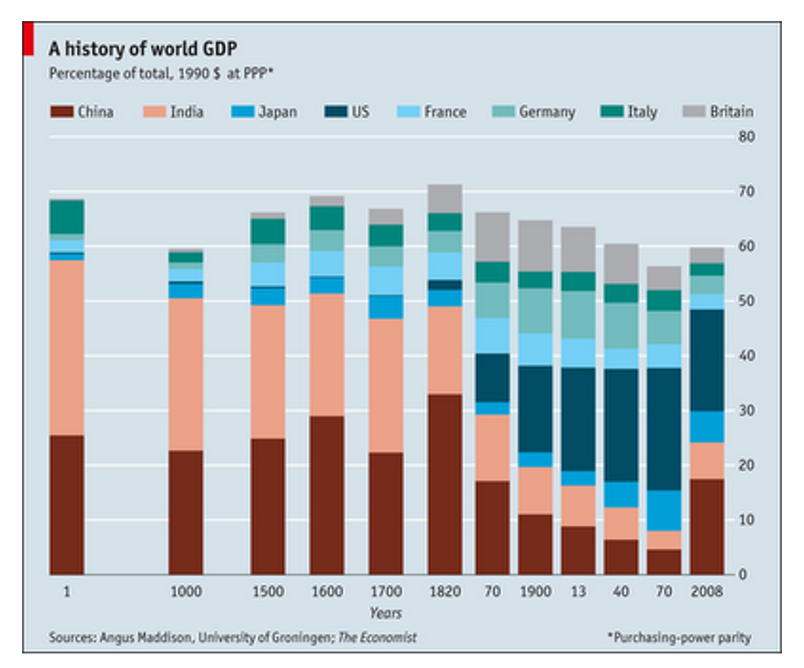
- shift in global center of economic gravity to core
- outsourcing has led to increasing manufacturing and low-skill service sector to semi-periphery
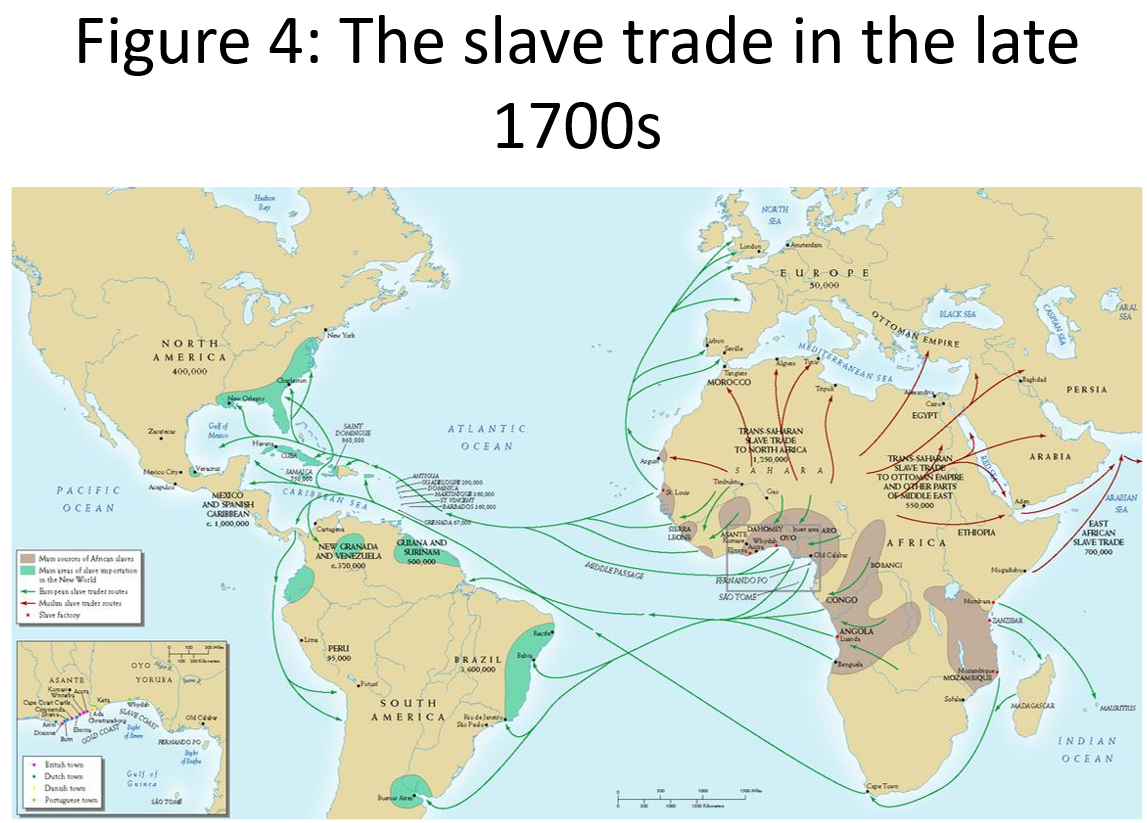
- Slavery and plantation economy
- farming, cropping, rotation, slash and burn heavily active in global south and periphery
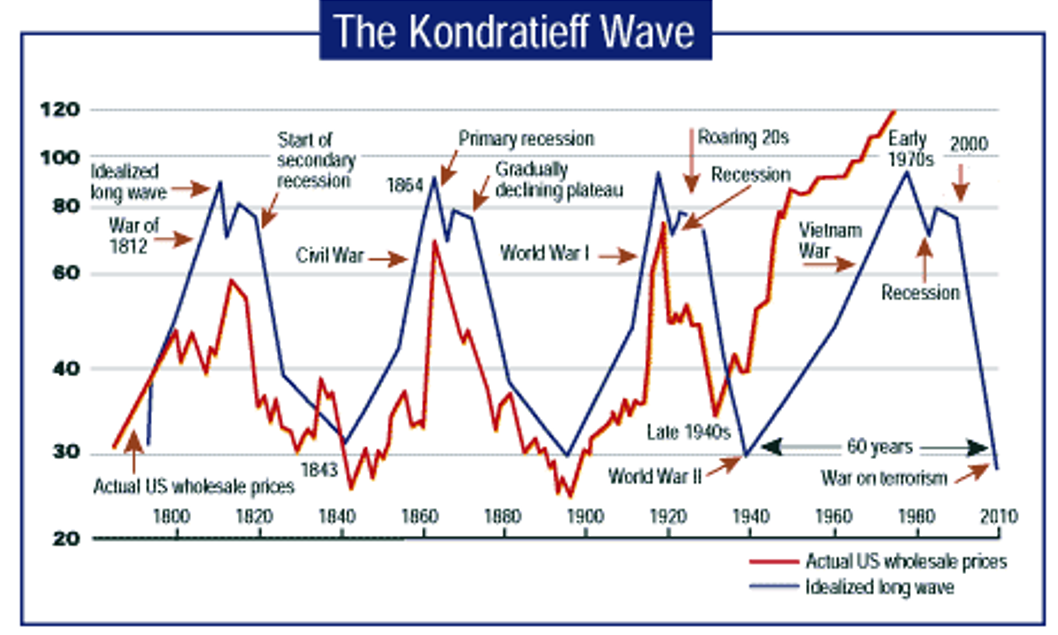
- Similar correlations with Kondratieff long-waves
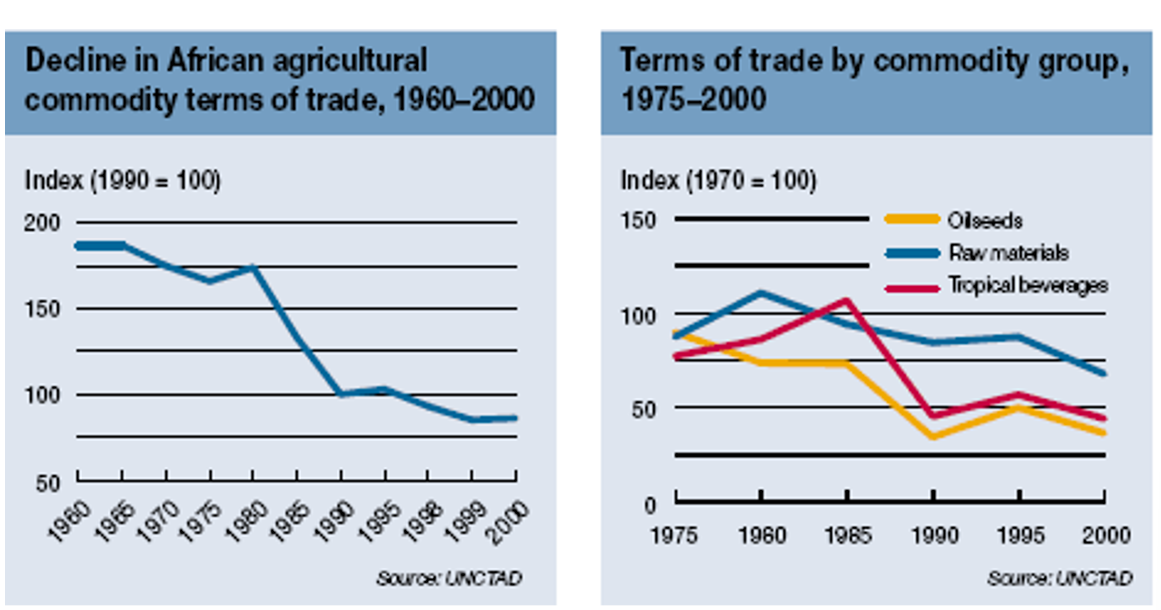
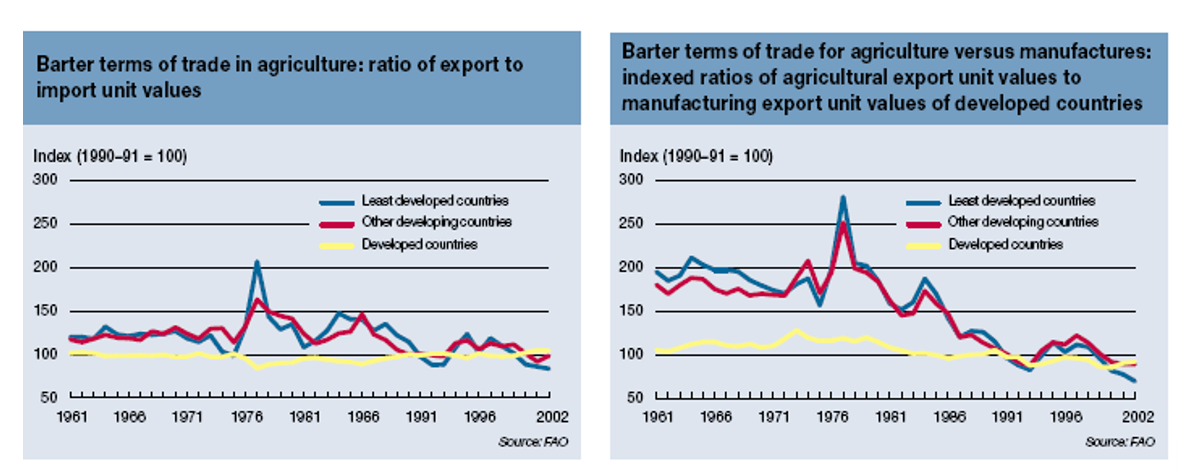
- 1940s - declining terms of trade for colonial and peripheral commodities
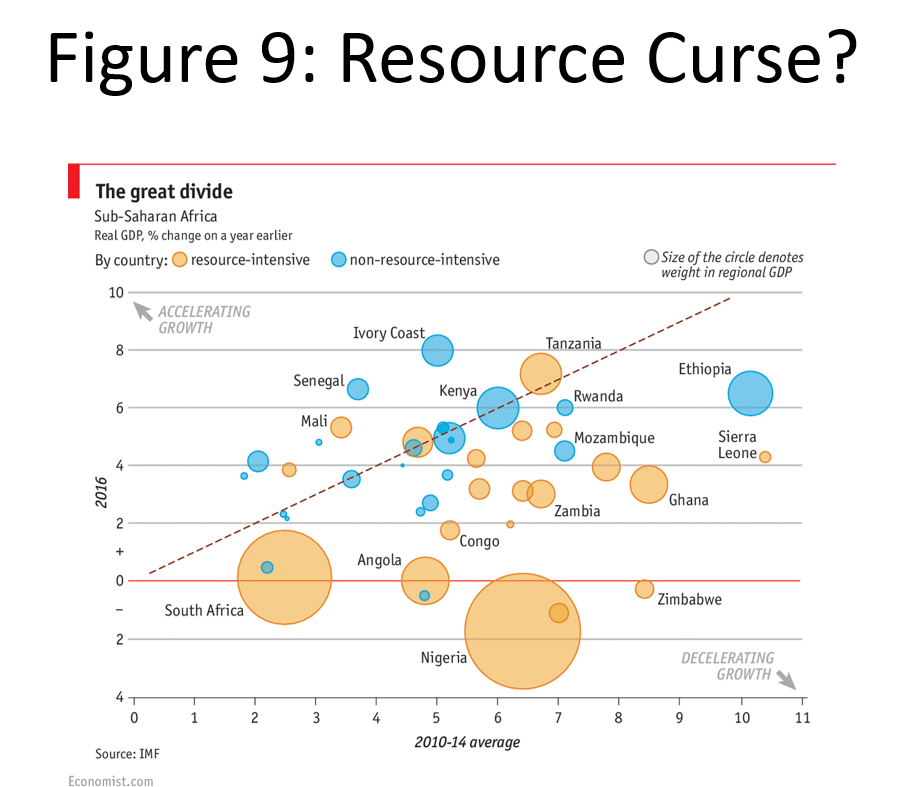
- Resource curse
1750-1970 Economic Realignment and geographic polarization
- 3 zones emerged: core, periphery, semi-periphery
- decline of manufacturing in colonized and colonial dominated countries
- investment in plantation agriculture and extraction of raw materials increased
- correlation of bursts of colonialism and Kondratieff troughs/downturns e.g. 1880s
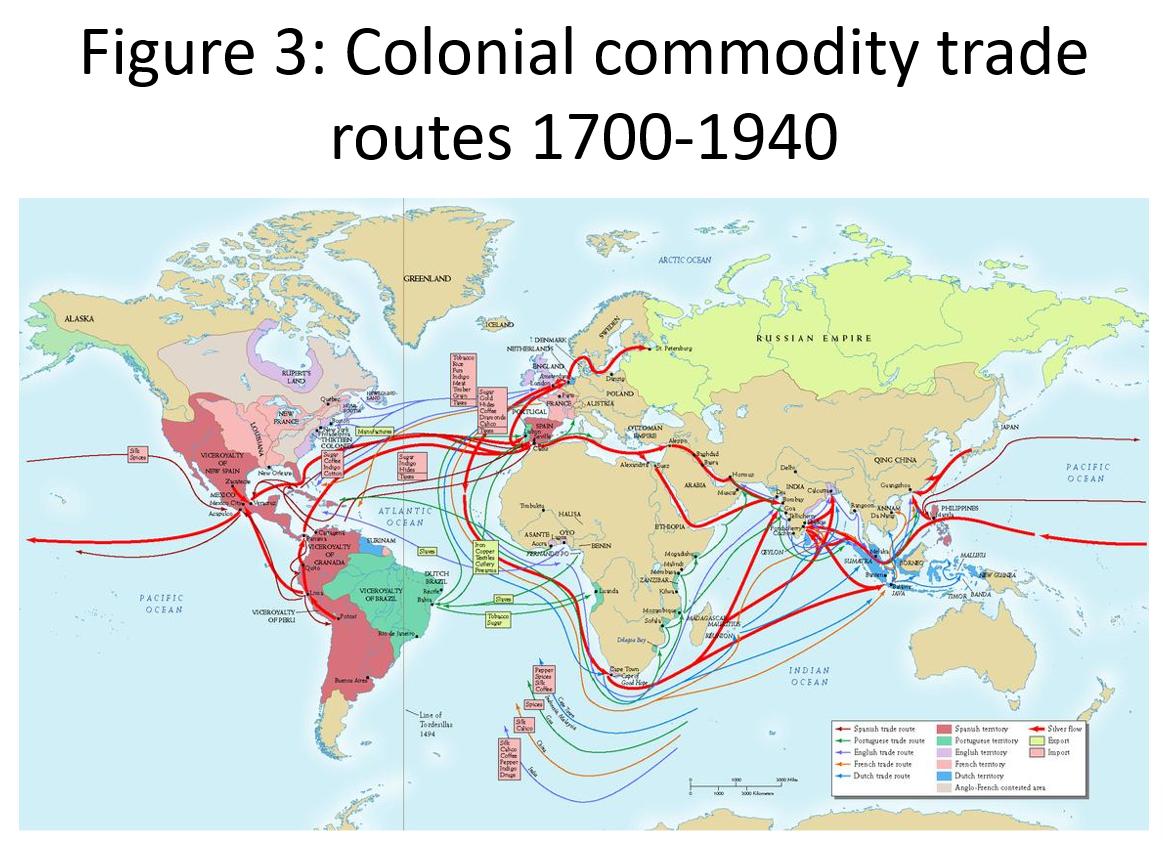
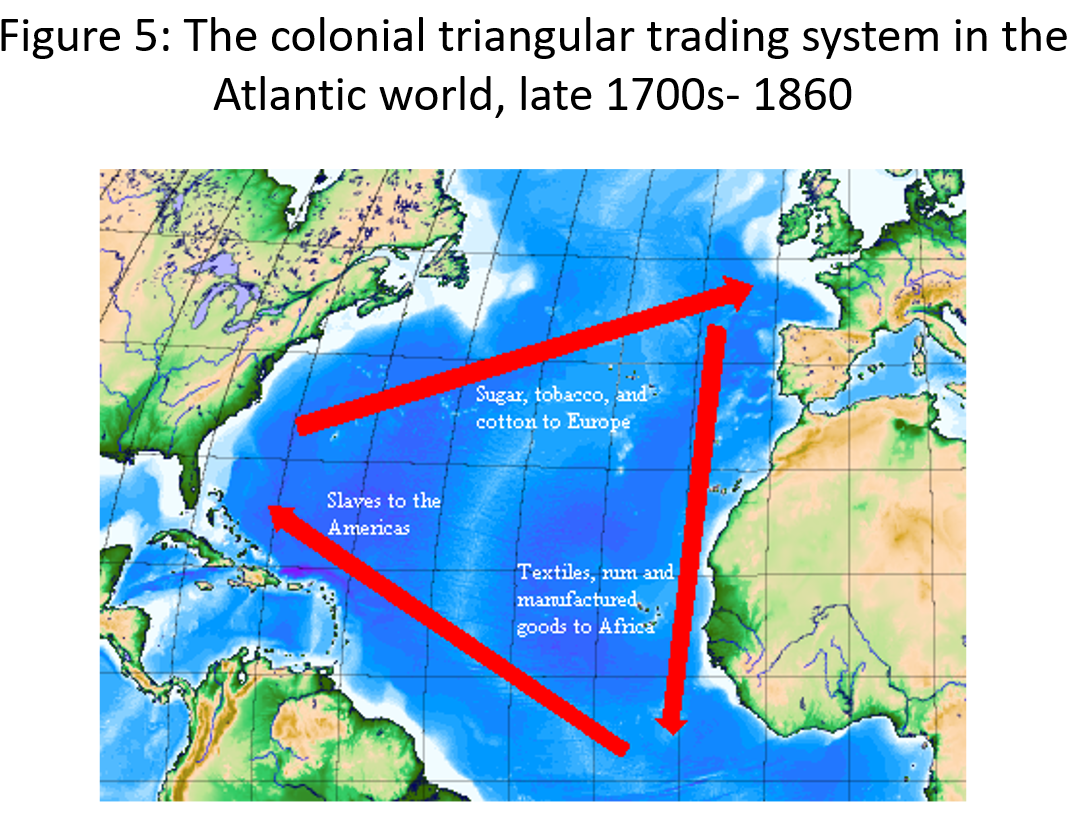
- three sided trading (triangular exchange) - raw mats from periphery -> Europe and US core; manufactured goods from core -> Britain empire; goods from britain -> periphery
- large countries w political independence: Mexico, Brazil, Argentina 1920s-30s - pursued import-substitution in semi-periphery
- 1940s-70s - political inmdependence for most of colonial world, Latin america after 1820s
- declining commodity and trade terms over time for basic commodities (1950s-70s)
- “resource curse” hypothesis - too much of a good thing e.g. argentina agri and Guinea oil -> easy money -> corruption -> no reason to diversify
- but, diversification raises exchange rate bc prices not in local currencies and makes improts more expensive
- across sub-saharan, resource intensive countries decelerating growth relative to those less dependent on export of basic raw materials