16 - Misc Rendering - Procedural, Particle, Volumetric
ucla | CS 174A | 2024-03-19 16:16
Table of Contents
Opacity
- introduce oopacity intensity 0-1 as
- apply this to color channels by multiplying over
Composition of colors
- layered polys can be composited colors based on opacity
- straight - factor out opacity, just get composite color
- pre-multiplied - assuming colors given after opacity multiplied, find olor aand alpha w saame algo

Procedural/Behavioral Models

Particle Rendering
 rendered as sprites, display color based on z-buffer or sprite which ever is on top render sprites (particles) always facing the front/camera
rendered as sprites, display color based on z-buffer or sprite which ever is on top render sprites (particles) always facing the front/camera 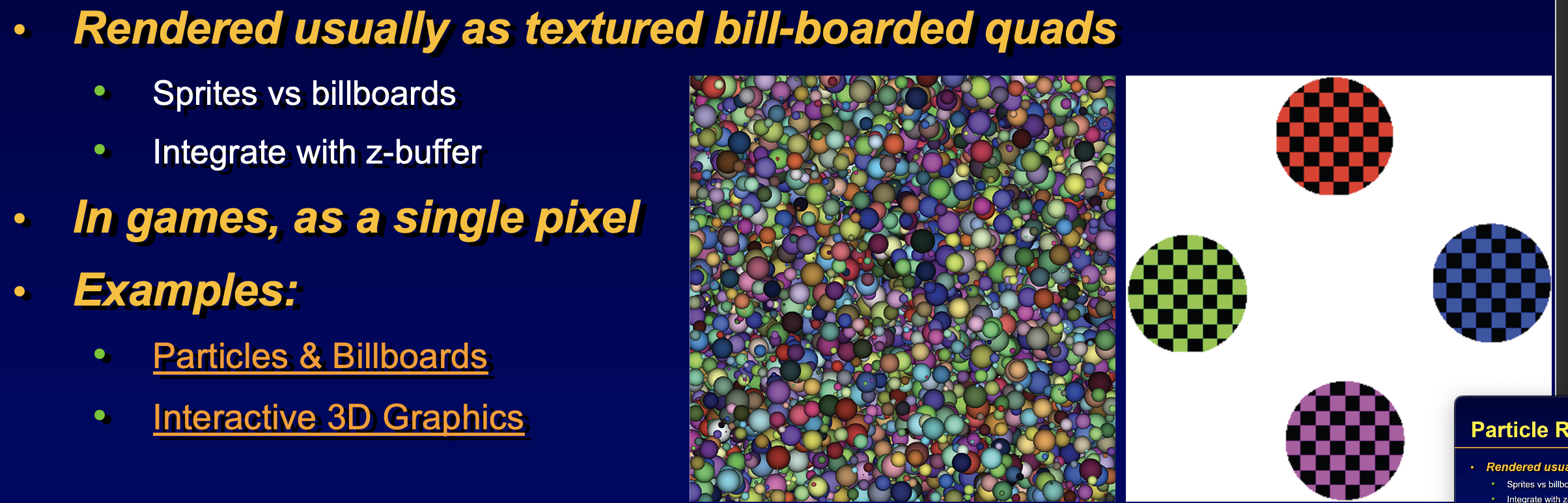
Volume Rendering
- tesselation make “hollow” objects
- volume rendering allows us to make “solid” objects that can be sliced and can be “entered”
- usually nothing but ray casting (non-recursive) and parallel projection
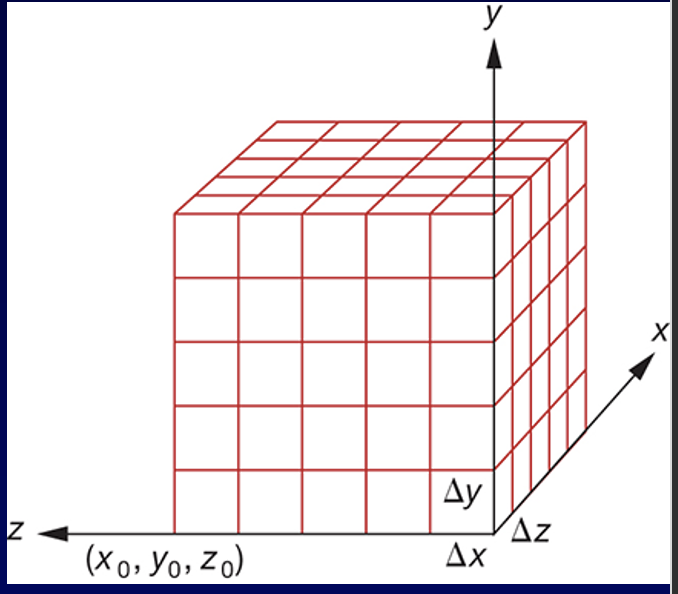
- discretize volumetric objects to elements called “voxels”
- makes a poly mesh of iso-surfaces by looking at voxel coords
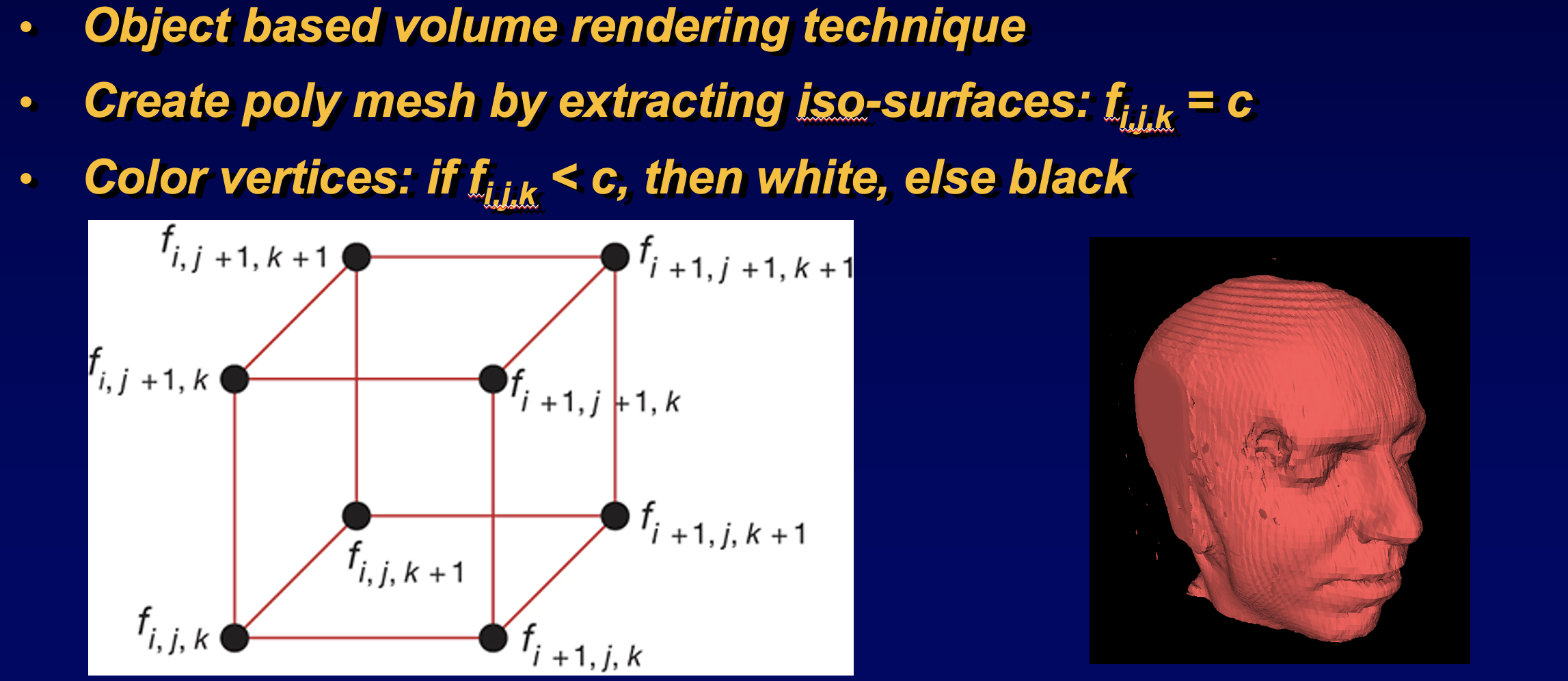
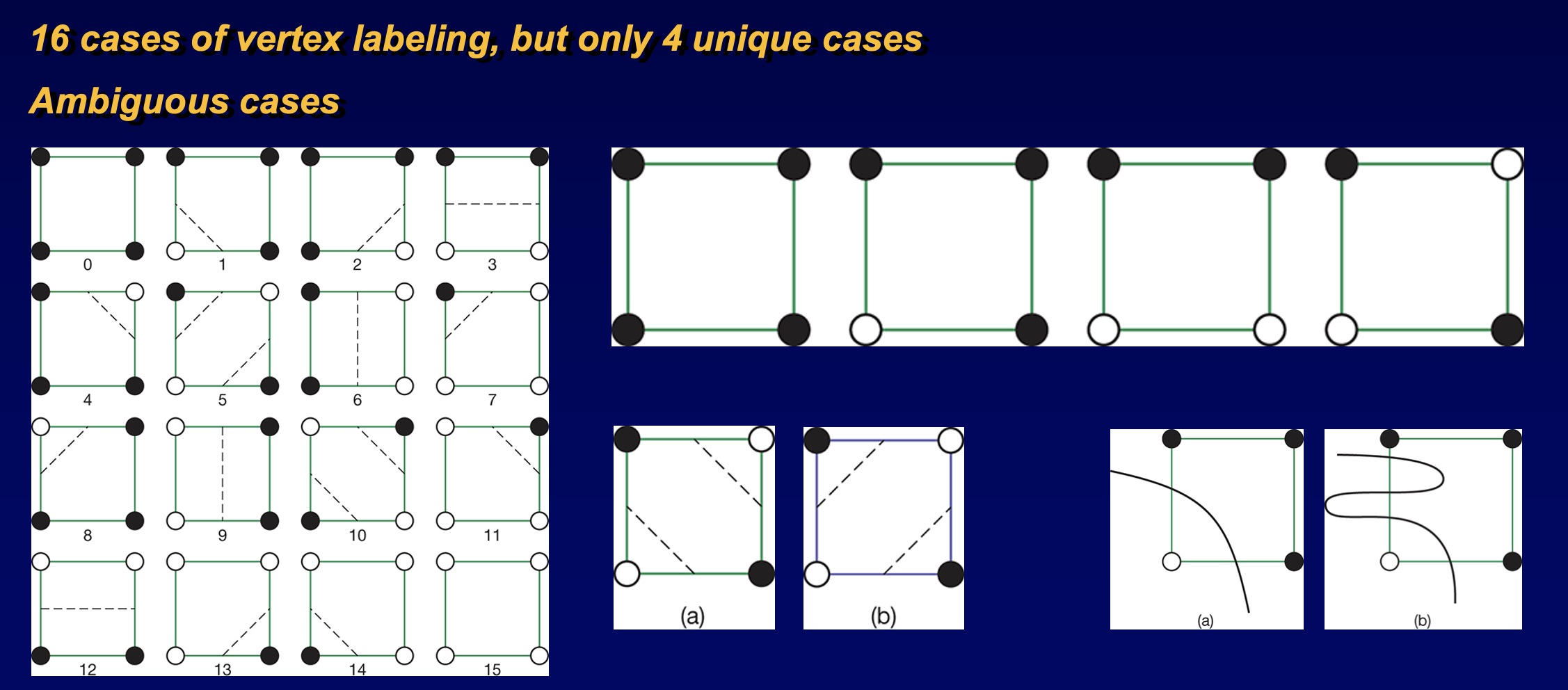
- iso surfaces in voxels:
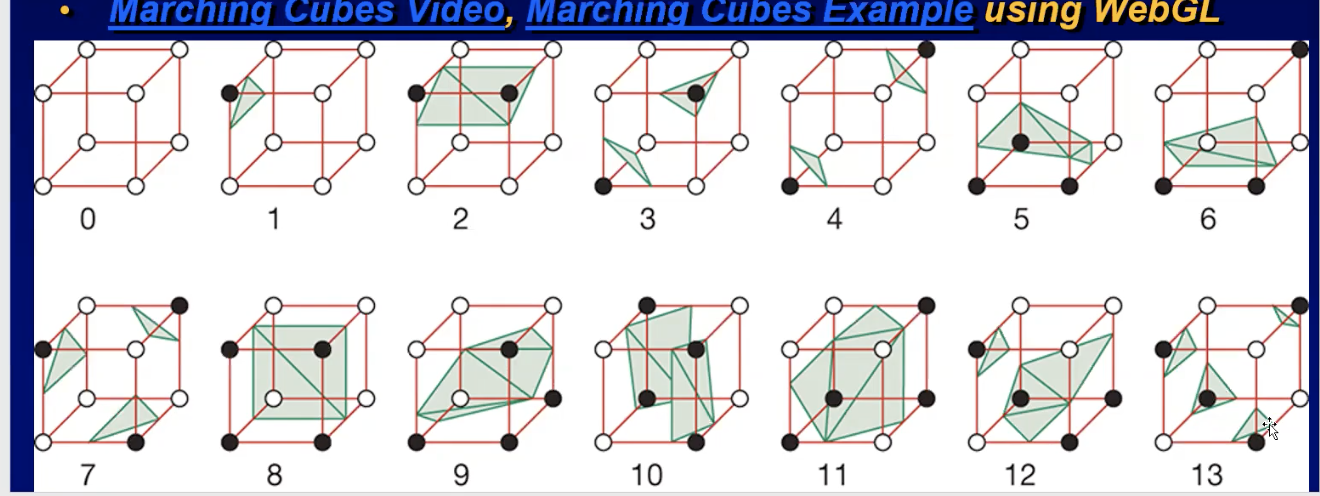
- e.g. 2D marching squares, check if the color or other property is greater than a threshold, then determine the cases to render
- “splat” the front facing (bc no PS) voxels of the object and composite (FTB or BTF) and splat it onto the screen to generate the footprint of the volumetric object

V-buffer
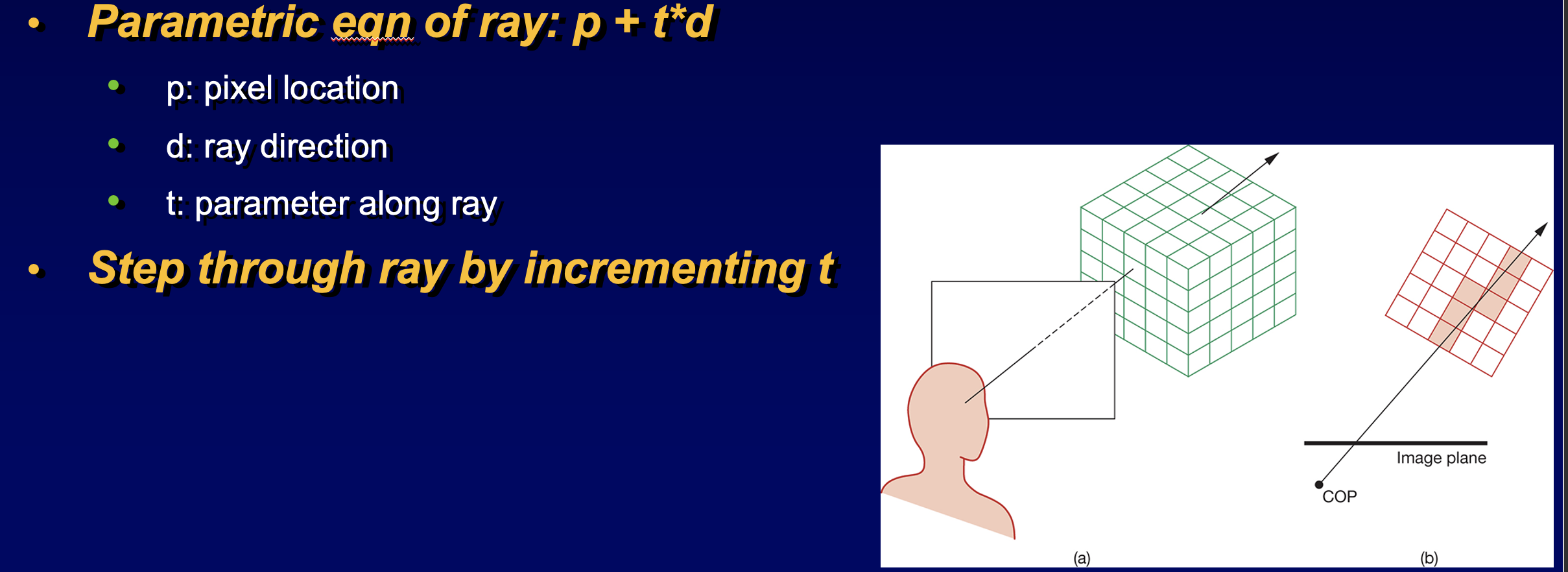
- ray cast from eye through volume
- trilinear interp for properties of non-vertex location of a voxel
- accumulate color and opacity as ray passes through the volume
- parallel ray cast through each pixel (in parallel), choose t as sampling rate to determine how many voxels along the ray you will sample
- color composition is done FTB so no backface culling, just do composition above
- determine color using composition aalgo
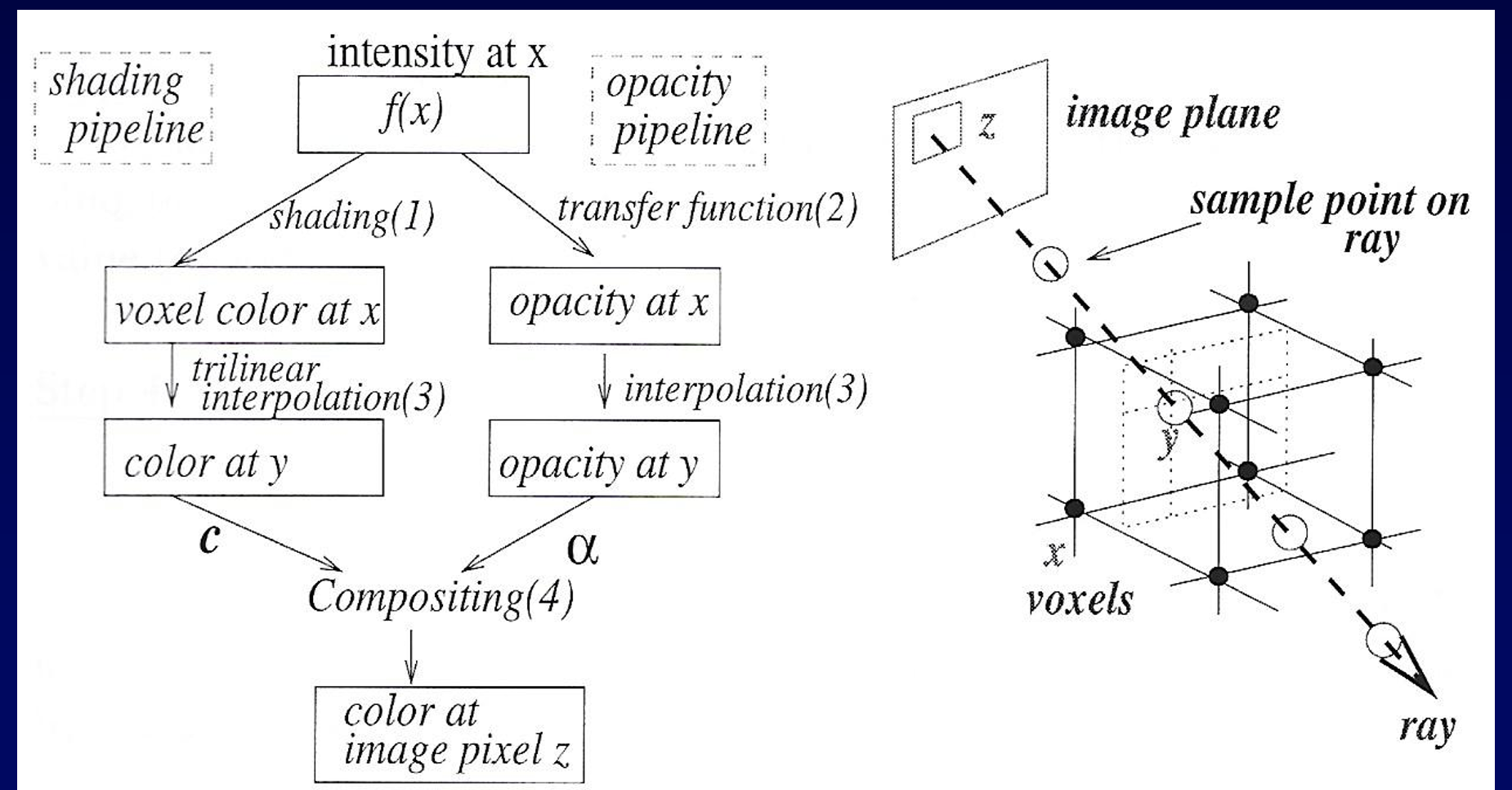
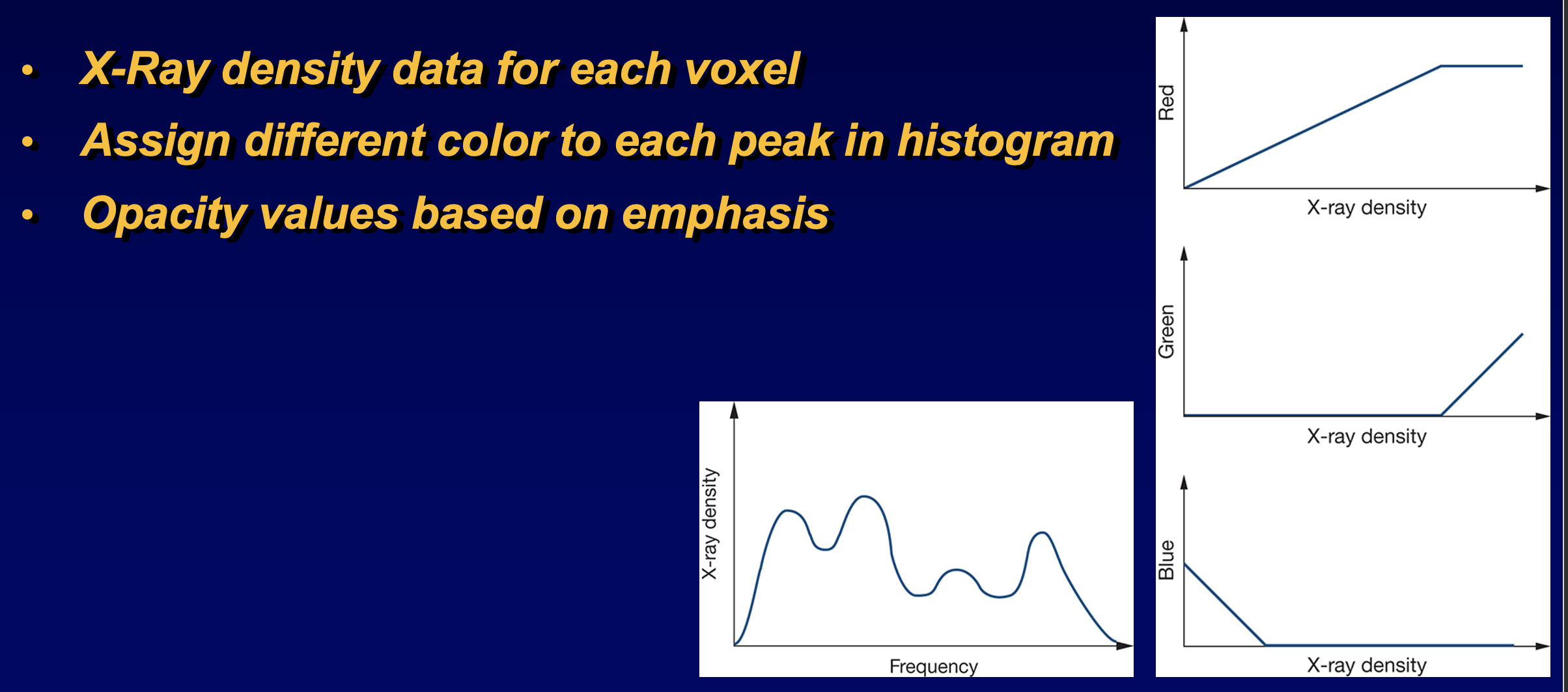
- where the transfer function can be specified
Optimization

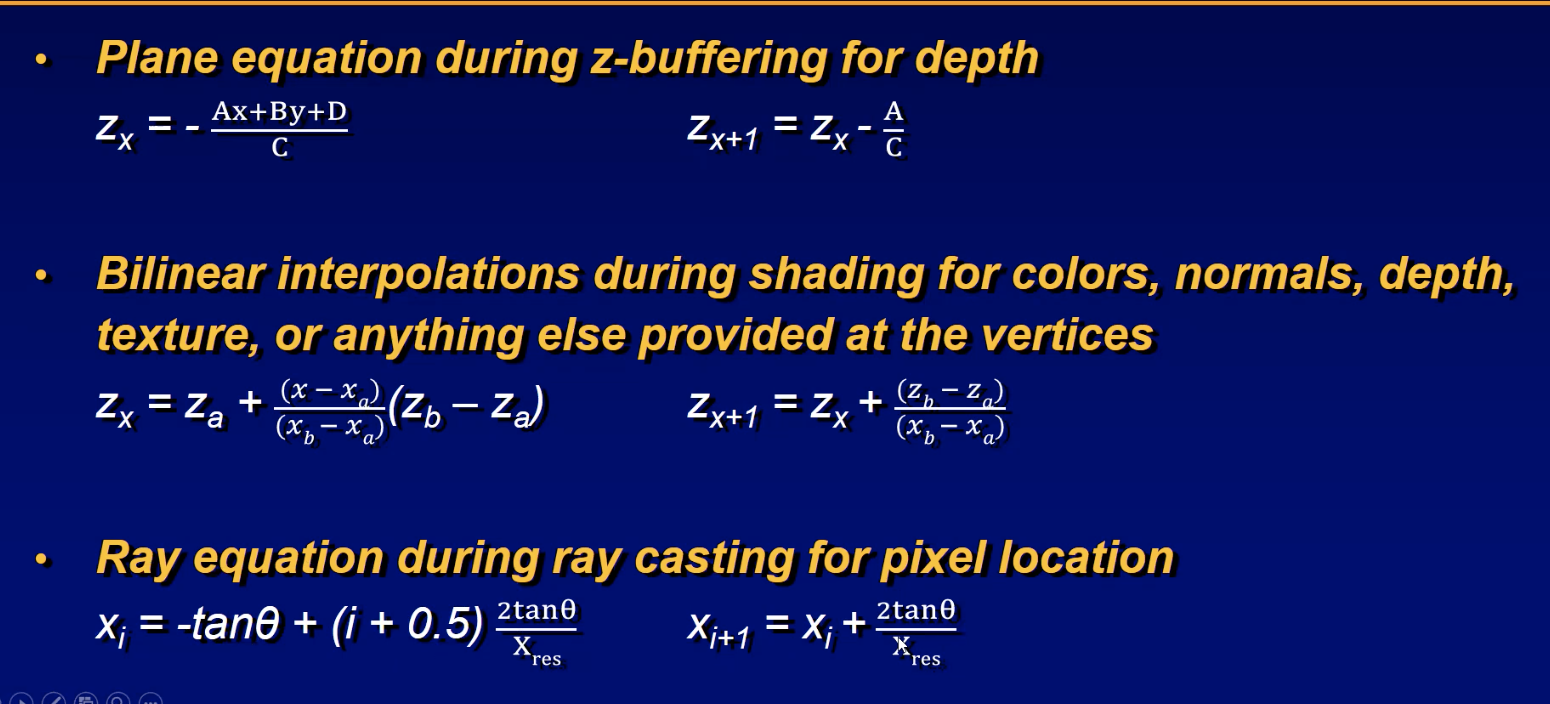
Incremental Formulas