12 - Scoreboarding
ucla | CS M151B | 2024-02-22 16:28
Table of Contents
Limitations of RAT (renaming regs)
- RAT resolves WAR and WAW dependencies but till not RAW
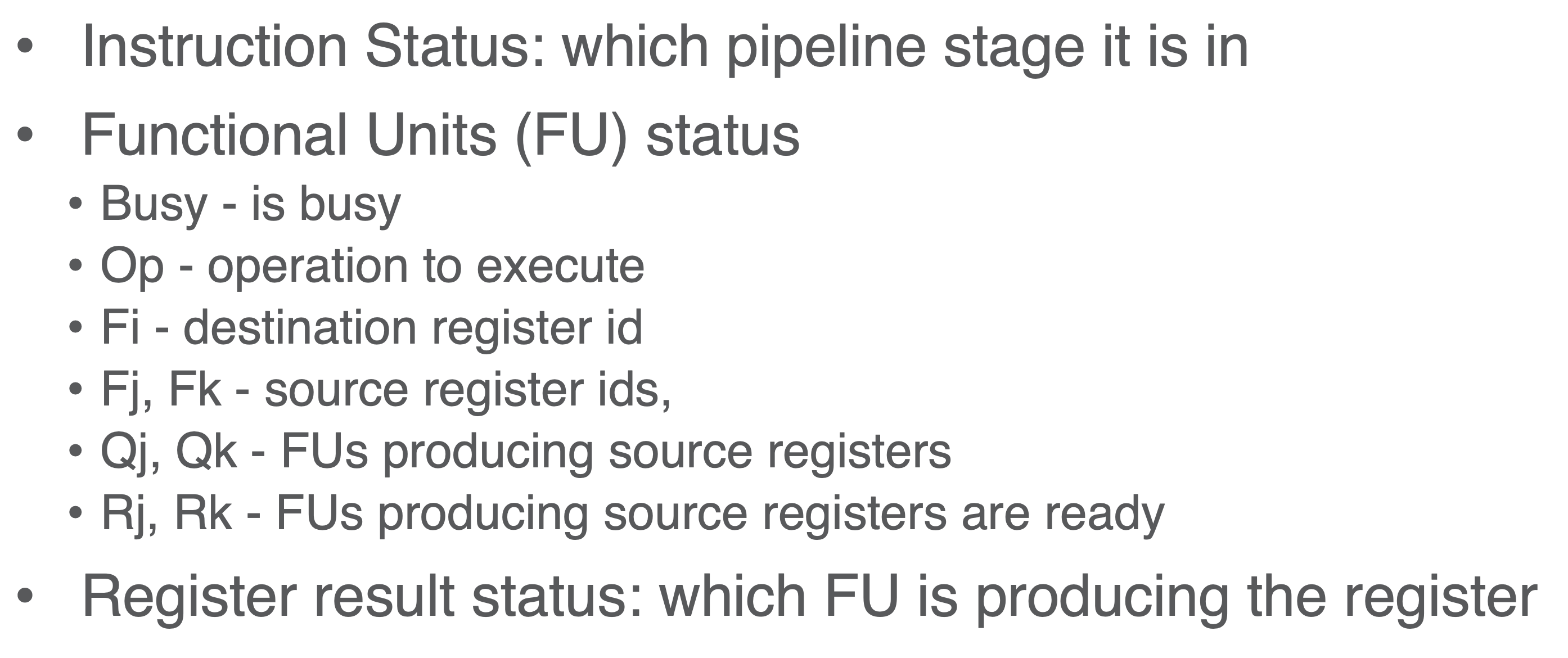
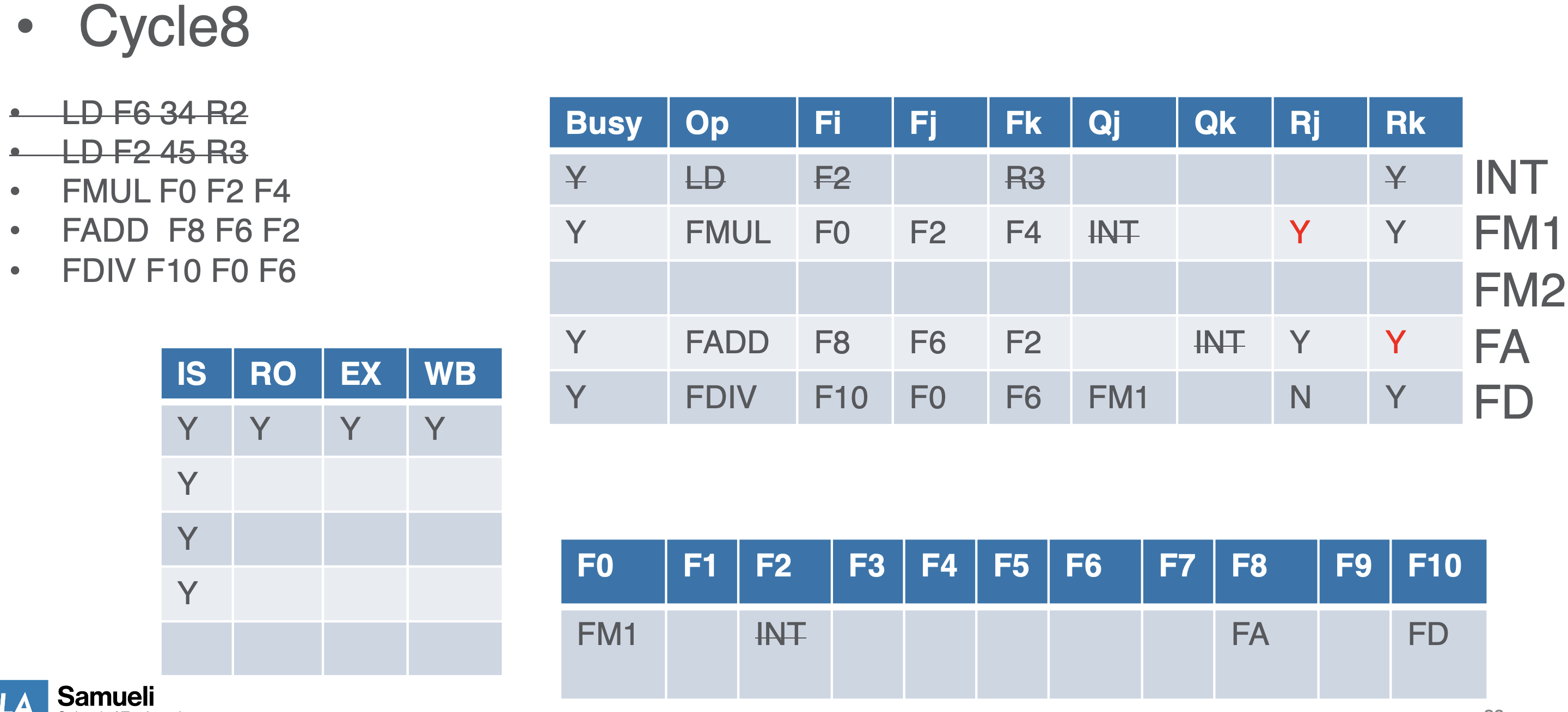
- we now add a scoreboard in the OOO exec step:
CDC6600 - First OOO proc
- has multiple fixed latency functional units (e.g., FP mult, div, add, sub)
4 stage pipeline
- Issue
- Fetch next instruction
- Wait for no hazards
- Data WAR: check if previous instruction is writing to any of my source operands
- Data WAW: check if previous instruction is writing to my destination operand
- Structural hazards: check if functional unit not available
- Reaad Operands
- read reg ffile
- Exec
- each FU execs
- mitigate RAW by waiting for source operand validity
- Writeback
- no regiter renaming
- WAR and WAW seen but stalls
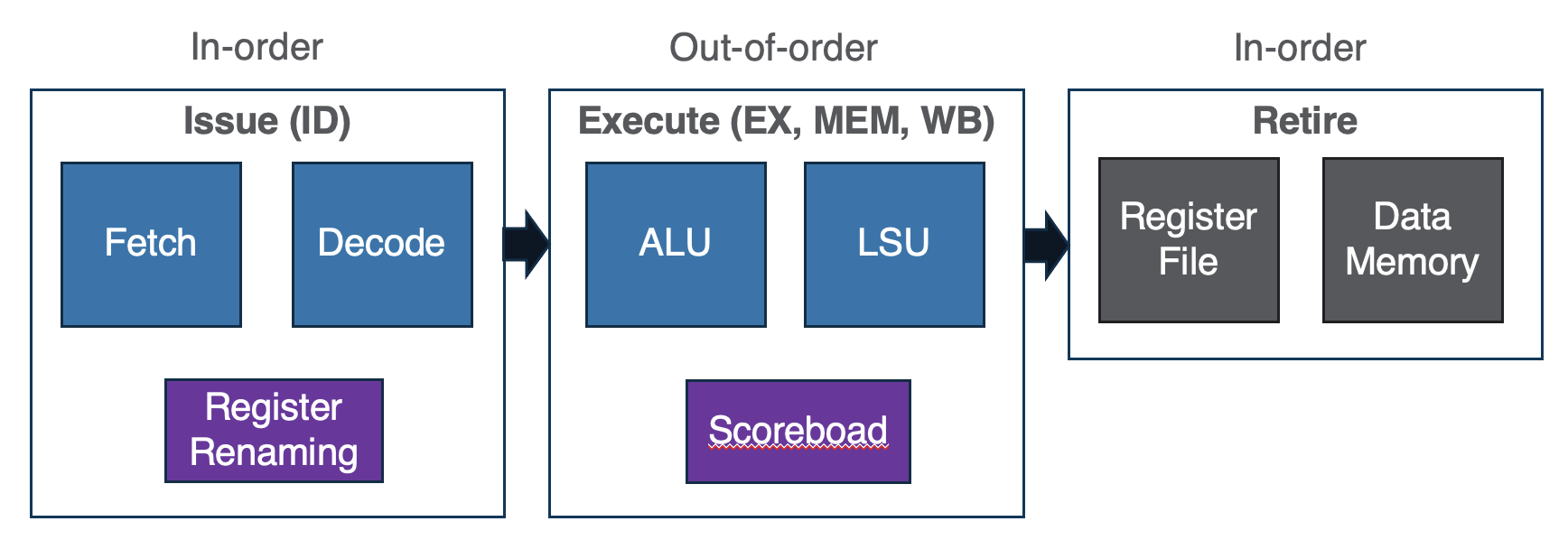
Tomasulo Algo
- track register dependency
- removes name dependency by renaming
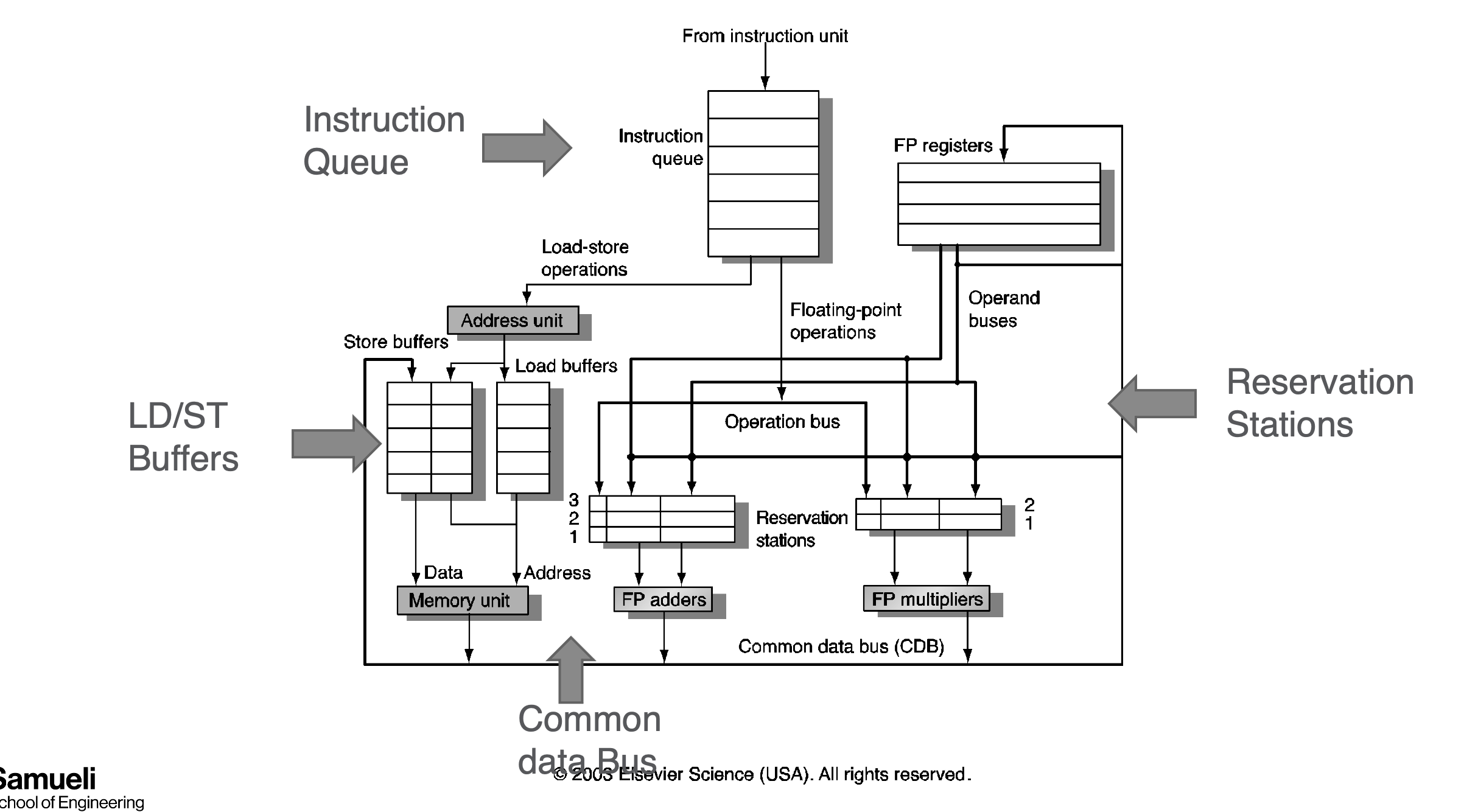
- 3 stages: isssue, exec, wb
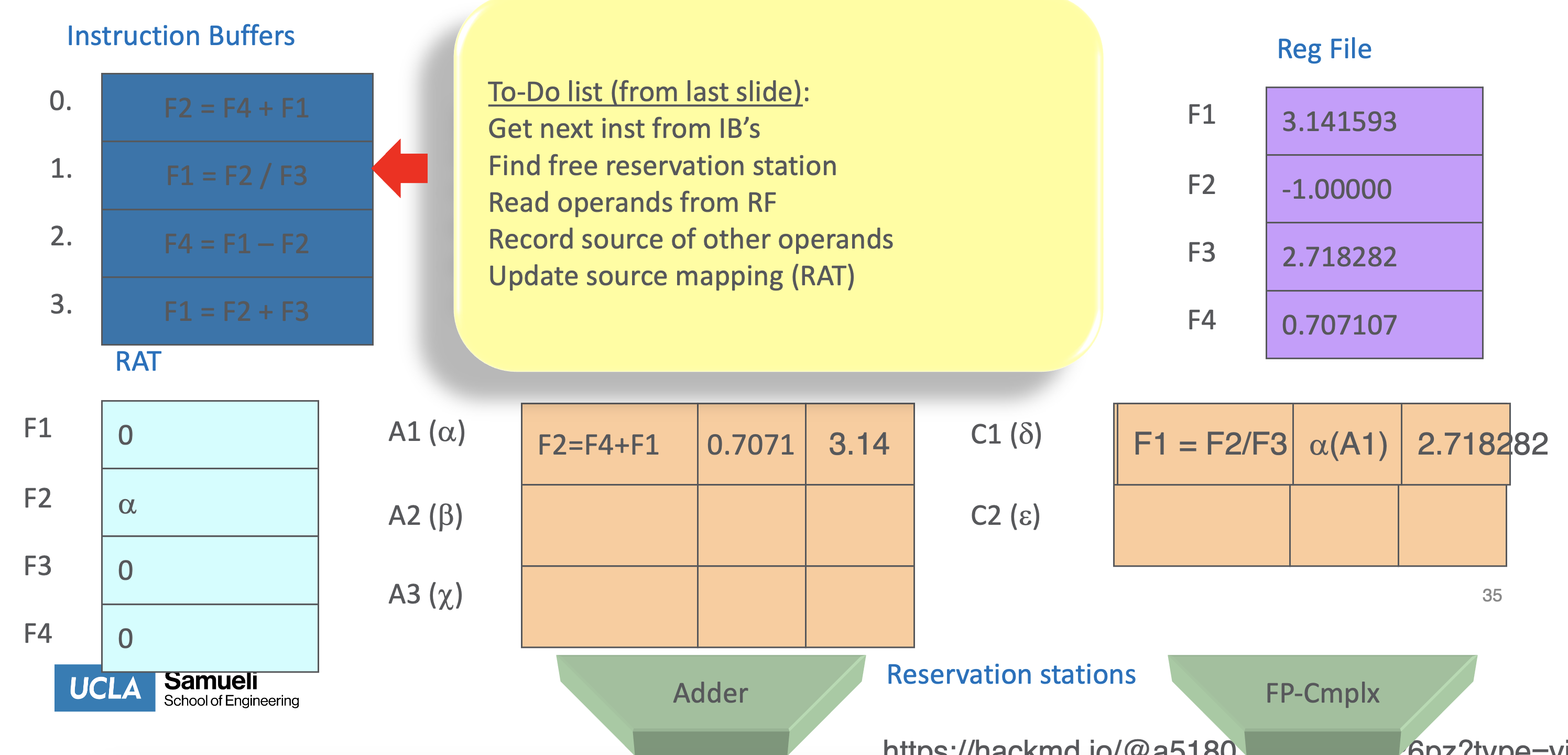
Issue
- Get next instruction from instruction queue.
- Find a free reservation station for it (if none are free, stall until one is)
- Read operands that are in the registers
- If the operand is not in the register, find which reservation station will produce it
- In effect, this step renames registers (reservation station IDs are “temporary” names)
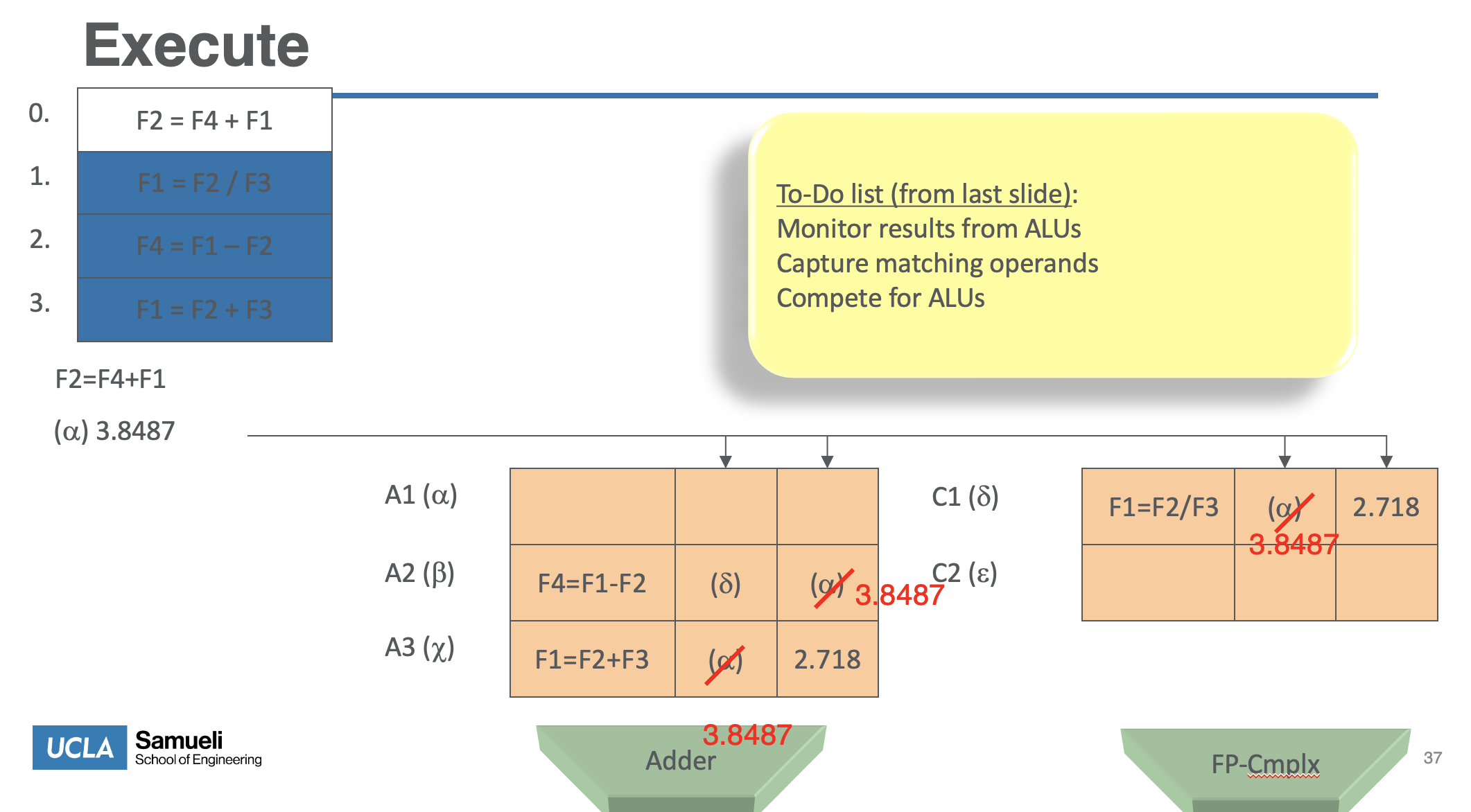
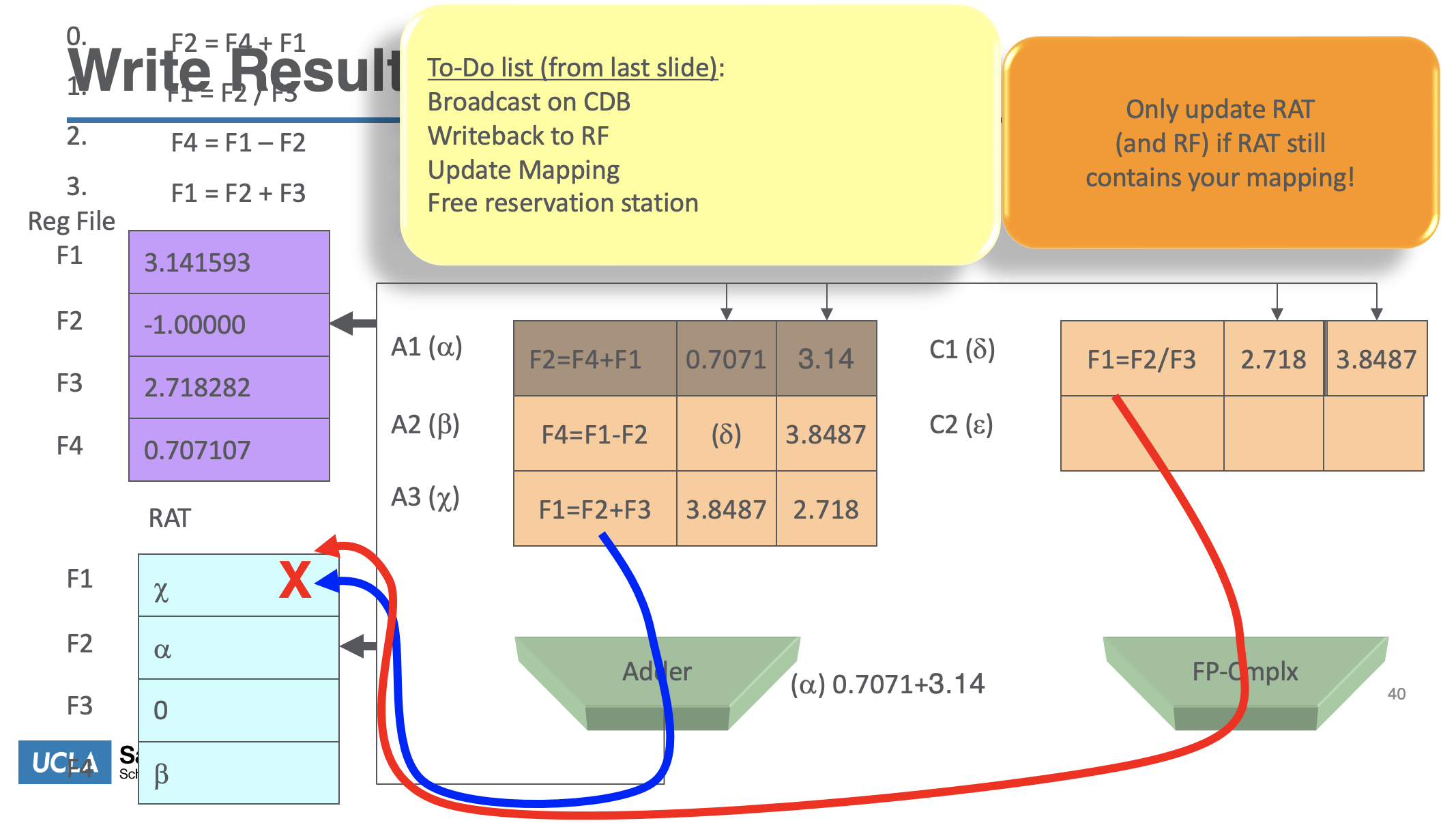
Exec
- Monitor results as they are produced
- Broadcast result to all reservation stations with operands waiting for it (via common data bus)
- When all operands available for an instruction, it is ready for execution.
- When multiple instructions in RS are ready?
- When result is computed, make it availableon the “common data bus” (CDB), where waiting reservation stations can pick it up
- Stores write to memory
- Result stored in the register file
- This step frees the reservation station
- For our register renaming, this recycles the temporary name (future instructions can again find the value in the actual register, until it is renamed again)
Load/Store
- The reservation stations take care of dependencies through registers.
- Dependences also possible through memory
Drawbacks
- Many associative stores (CDB) at high speed
- Performance limited by Common Data Bus
- Multiple CDBs => more FU logic for parallel associative stores