2 - Abstraction and Computing Architectures
ucla | CS M151B | 2024-01-11 16:10
Table of Contents
- Abstraction
- Von Neumann Architecture
- Harvard Architecture
- Von Neumann Bottleneck
- Writing Programs
- Computer Execution Model
Abstraction
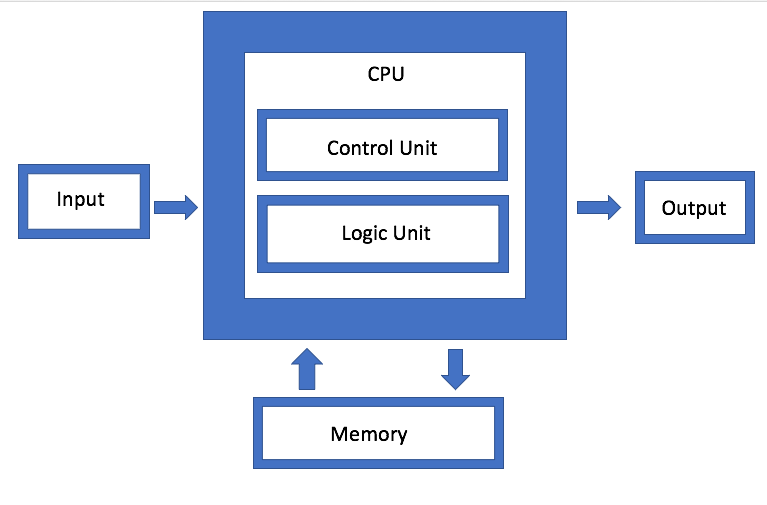
- hardware abstraction
- a computing architecture that introduced a CPU to process input -> output
- CPU consists of a control unit and an ALU
- also introduced a single address space in the memory unit that stores, instructions, inputs/outputs, data - allows simple control logic and a shared system bus
- there is a program counter PC register that tracks the address of the first instruction
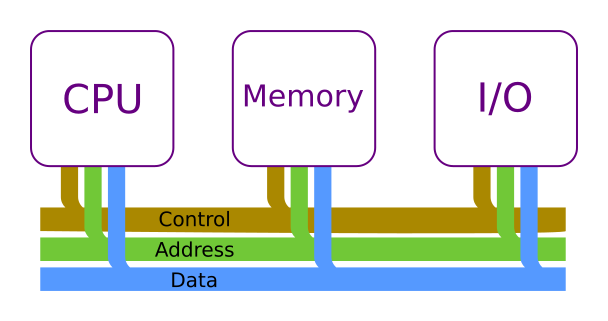
System Bus
- a bus - a set of connections that allows multiple component connections to the CPU
- address bus - specifies memory addresses
- data bus - specify data to transfer
- control bus - schedule transfer of data, selects which component can write to memory at a time
- shared bus has limitations in control switching and bottlenecks from throughput
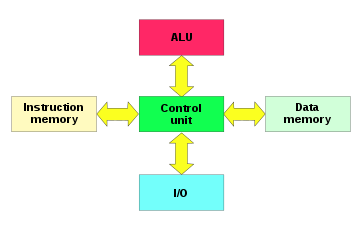
Harvard Architecture
- computing architecture to reduce bottleneck of von Neumann arch
- separate memory buses -> instruction memory and data memory
- limitations
- more expensive to store memory separately
- non-flexible address space if application uses more or less of one memory than the other
- advantages
- simultaneous access of instructions and data
- can specialize memory - e.g., make instructions read only, make data read/write, make some non-volatile an some volatile
- but still didnt solve von Neumann bottle neck
Von Neumann Bottleneck
- lagging memory and I/o access in terms of cycles while CPU is very fast
- long idle times for CPU
Mitigations
- caching - instruction and data cache
- on-chip memory
- I/O - bypass
Caching
- Instruction cache and data cache
- caches use SRAM (6 transistor faster but more expensive)
- memory uses DRAM (1 transistor slower but les expensive)
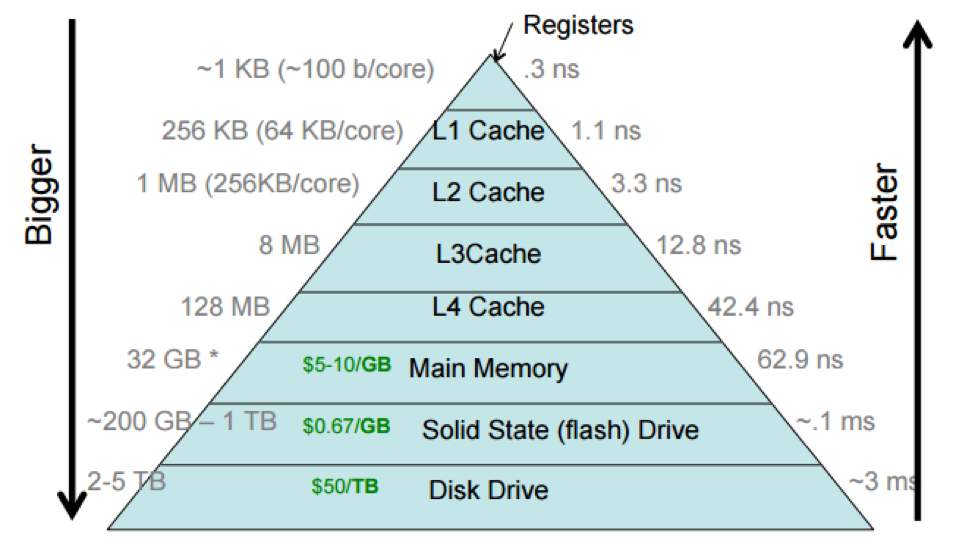
Memory Wall
- Cache levels:
- register
- L1,L2,L3,L4 cache
- Memory
- Disk
- speeds decrease as we go down
Writing Programs
- high level langs compiled to assembly - mostly for readability -> assembler to machine code and optimizations
- so to make certain optimizations we introduce an ABI between the compiler and OS kernel
- Application Binary Interface
- binaries compatibility bw OS for apps based on a contract bw SW and OS
- function call conventions, stack frame organization, binary object format
- Instruction Set Architecture
- Fetch: fetch next instruction using address from PC
- Decode: decode opcode and operands
- Execute: perform operation
- Update: update state/memory