Midterm Review
ucla | CS M151B | 2024-02-07 18:13
Table of Contents
- Latches and Data Forwarding
- Data Forwarding Decision Making
- Big Endian vs Little Endian
- Example Question
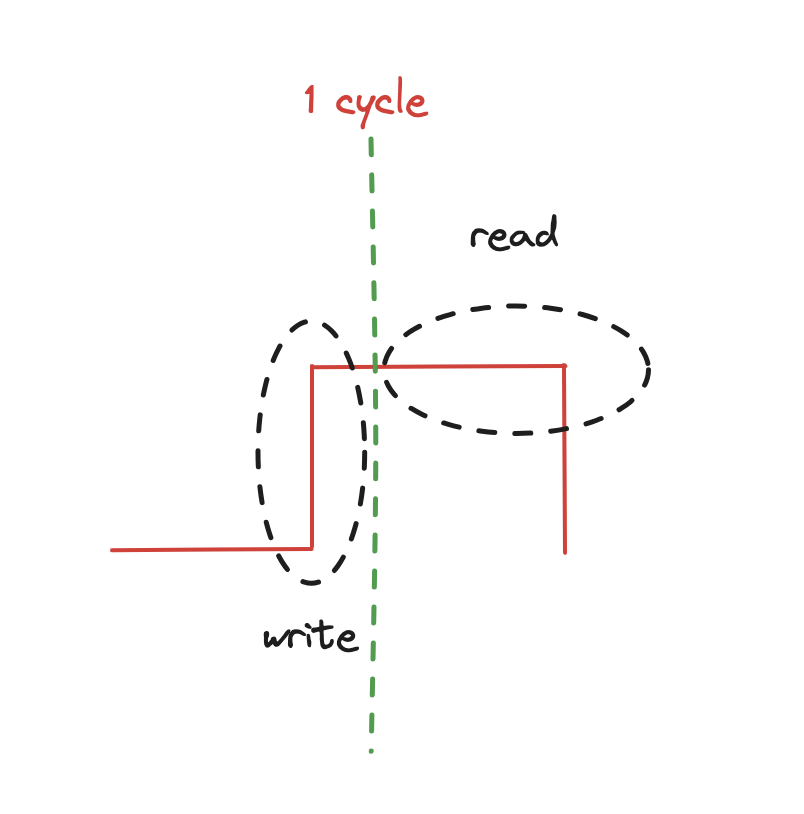
Latches and Data Forwarding
- latches are actual SR latches and read/write in the same cycle to push data forward to mux - read is combinational so we can do both in same cycle (second half)
- w/o data forwarding requires 2 NOPs so that writeback of first op happens at same cycle as read of next op (writeback happens on posedge - first half, then read happens on second half - combinational)
- w/ data forwarding only 1 NOP needed if theres dependency
- 0 NOPs if it is 2 consecutive ALU ops w/ data forwarding dependency
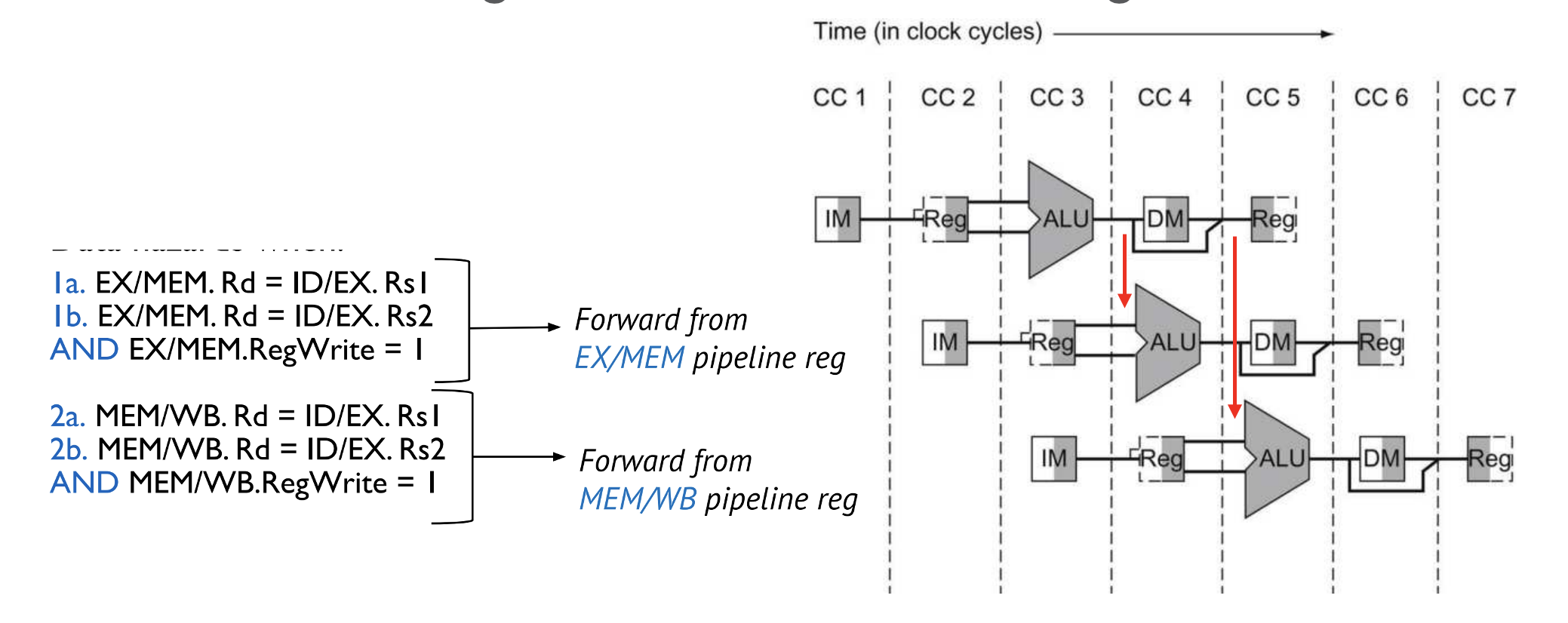
Data Forwarding Decision Making
- theres two paths of data forwarding (or backpropagating) but this design is better for signal propogation:
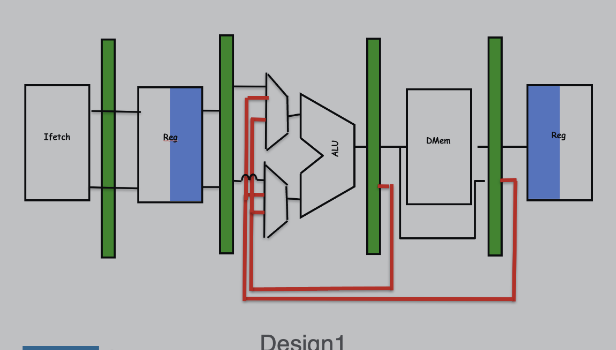
- M/W latch -> Ex
- Ex/M latch -> Ex
if (M/W.regWrite == True) && (F/Ex.rs1 == M/W.rd) || (F/Ex.rs2 == M/W.rd) { dataForward = True; } ^ chek same for Ex/M reg if 2 consecutive adds
-
regWriteis a flag to check whether writing is even occuring - then check the prev op dest reg
M/W.rdw/ each of the next op’s operand regsF/Ex.rs1 or F/x.rs2 - depending on the 2 ops, then check either Ex/M or M/W of first reg
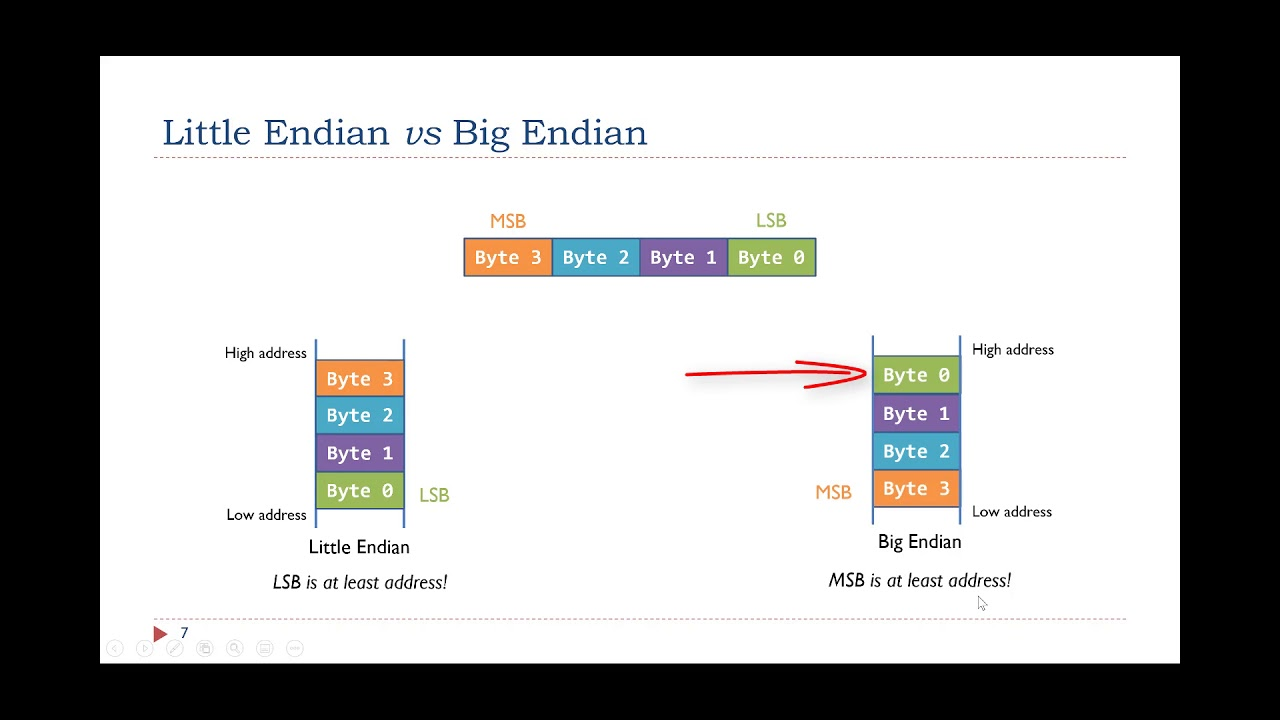
Big Endian vs Little Endian
Example Question
lb x6, 0(x7)
sd x6, 8(x7)
x7 -> 0x10000000 (addr)
0x10000000 -> 0x11_22_33_44_55_66_77_88 (val)
Whats at 8(x7) in BE and LE
BE:
x6 -> 0x00_00_00_11
8(x7) -> 0x00
LE:
x6 -> 0xFF_FF_FF_88
8(x7) -> 0x88
9(x7) -> 0xFF
...
- What’s at
8(x7)in:- Little Endian?
- Big Endian?