07 - Code Generation
ucla | CS 130 | 2024-11-20
Table of Contents
Model Driven Development
- forward engineering - model to code gen
- backward engineering - code to model gen
- Model based dev/engineering
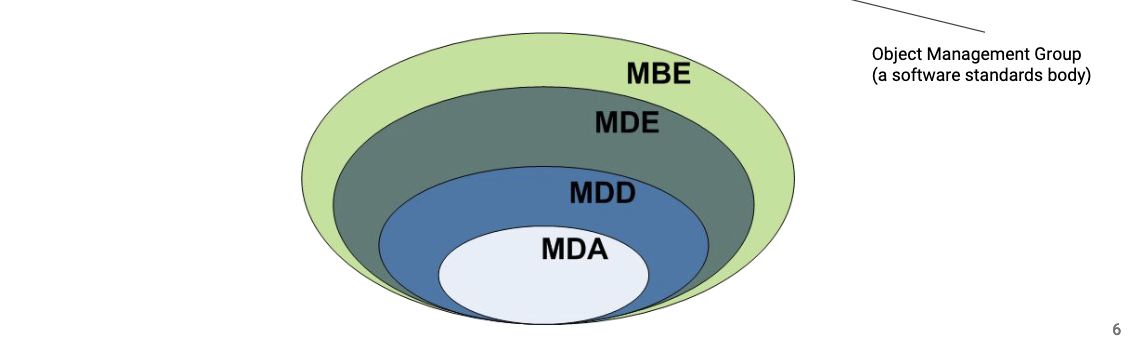
- models are abstractions of sw before dev and can be used to automate dev
- model is abstracted using generic modeling language like UML or domain specific (DSL)
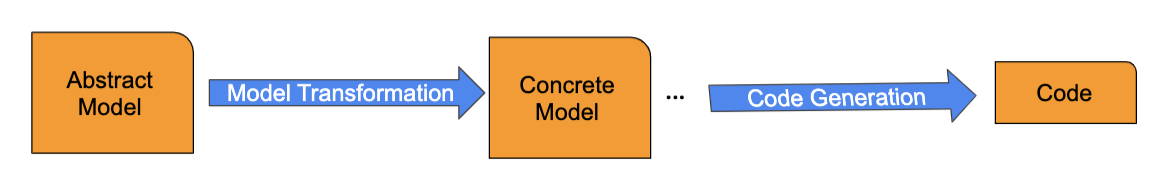
- models can be transformed to code automatically using a concrete model
Pro v Con
- Pros
- productivity - multiple uses of the same model
- simplification - SoT is model not code -> easier to analyze
- portability - same model can be used for diff langs/os/frameworks
- consistency - gen code is more conistent
- Cons
- Maintenance - must develop and maintain code generator
- Complexity - generated code may be less optimal and more complex than MVP
Code Generators
- code gen arch
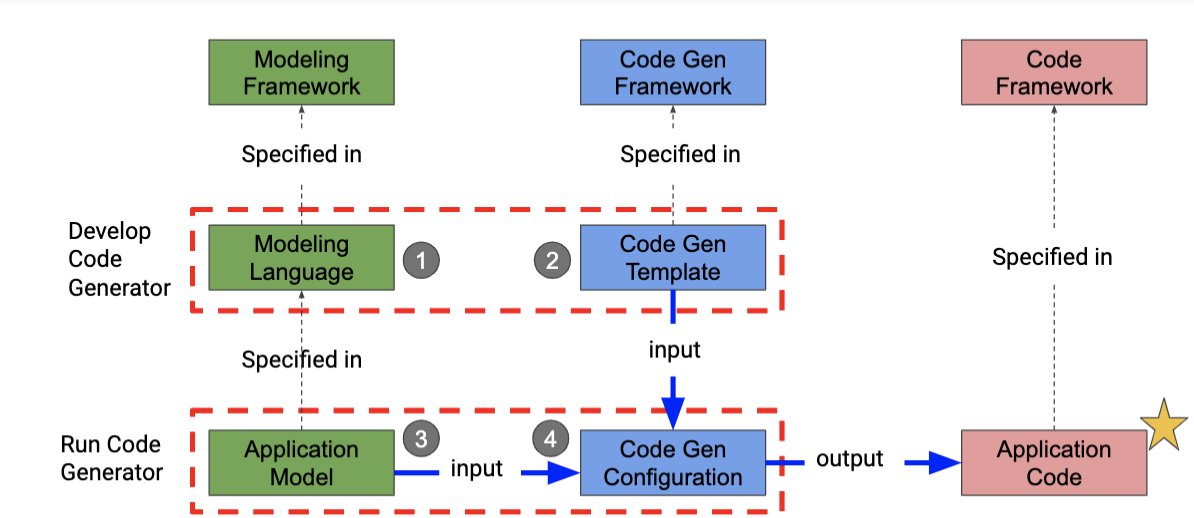
- Developing a code gen
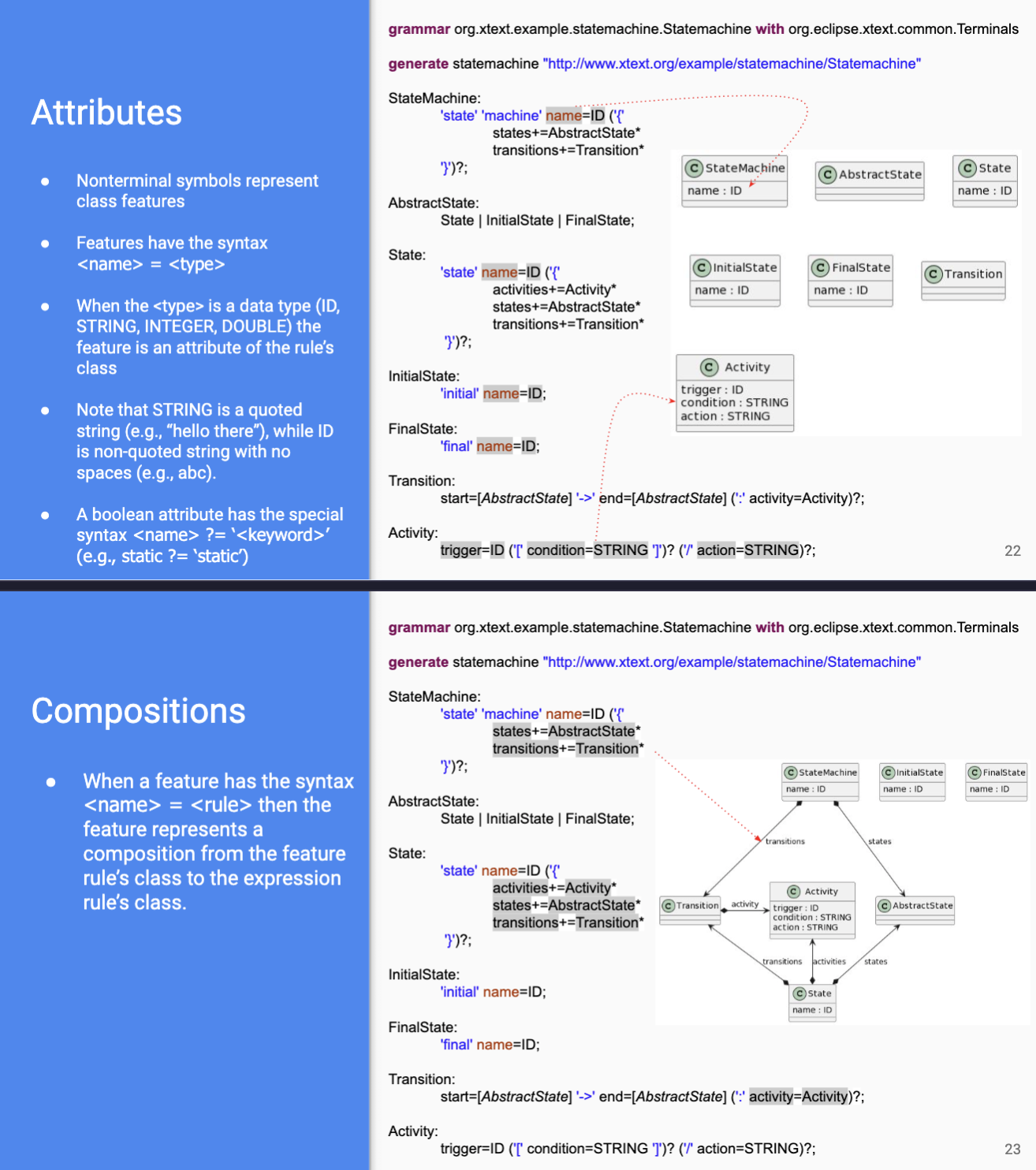
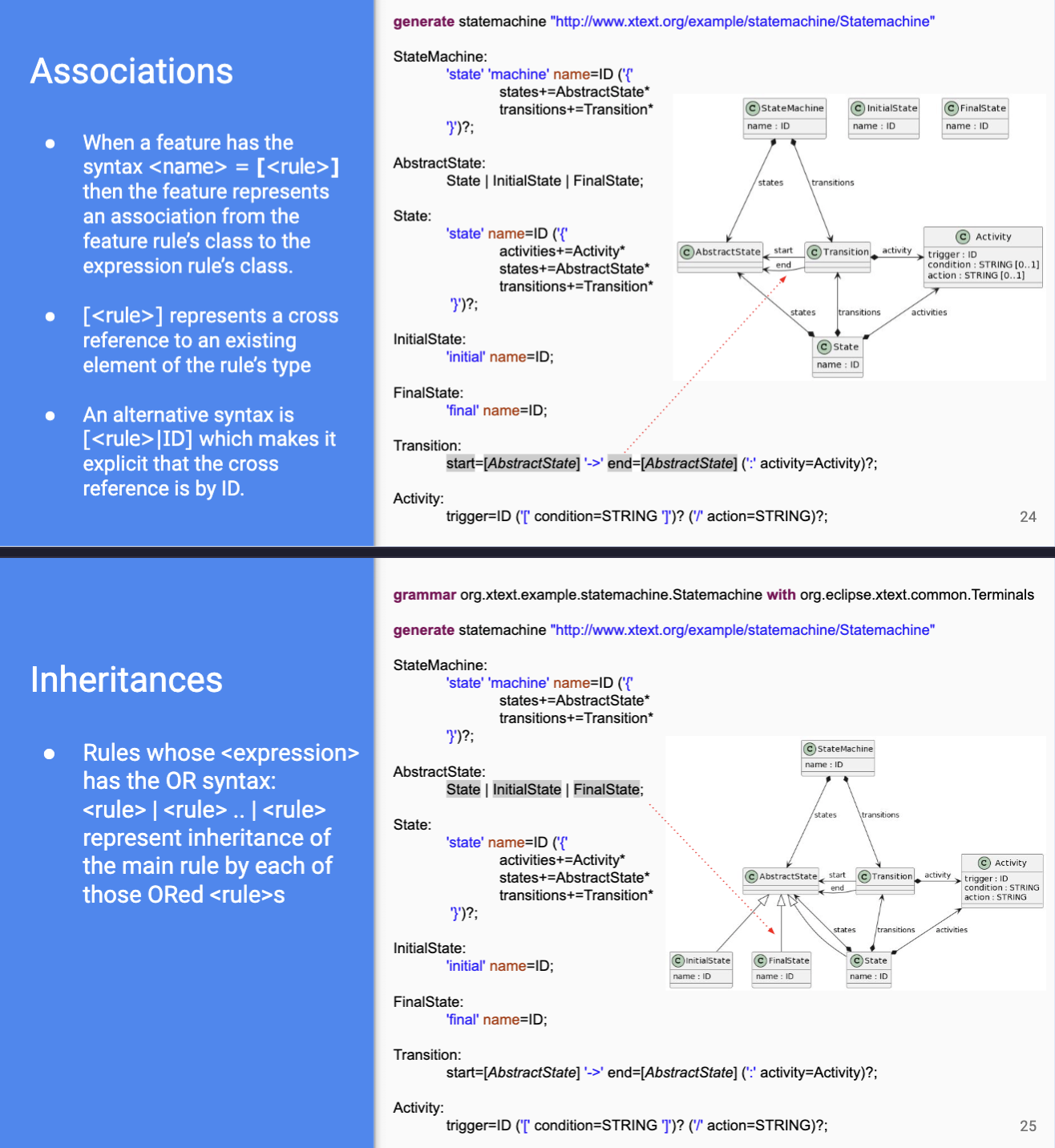
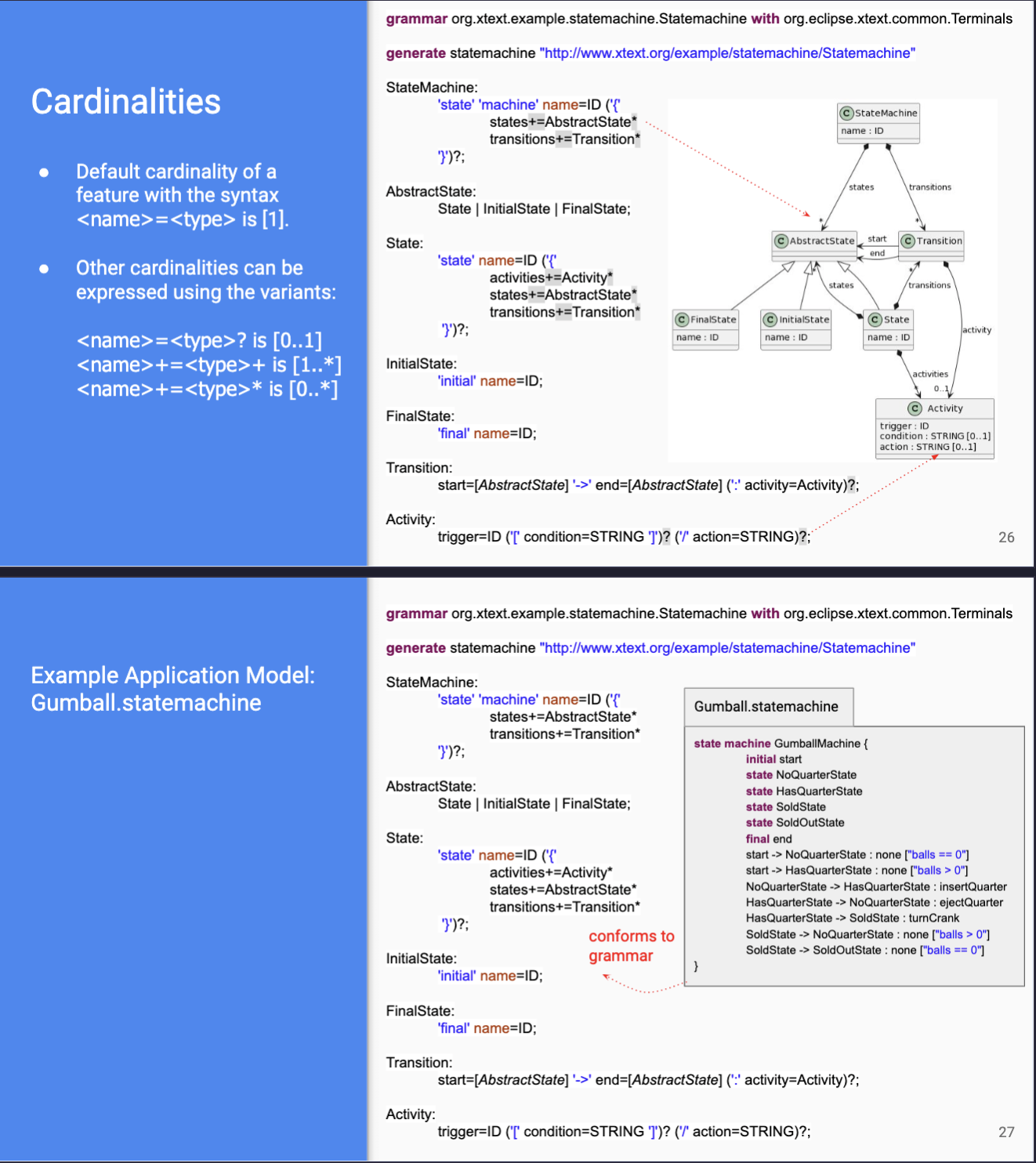
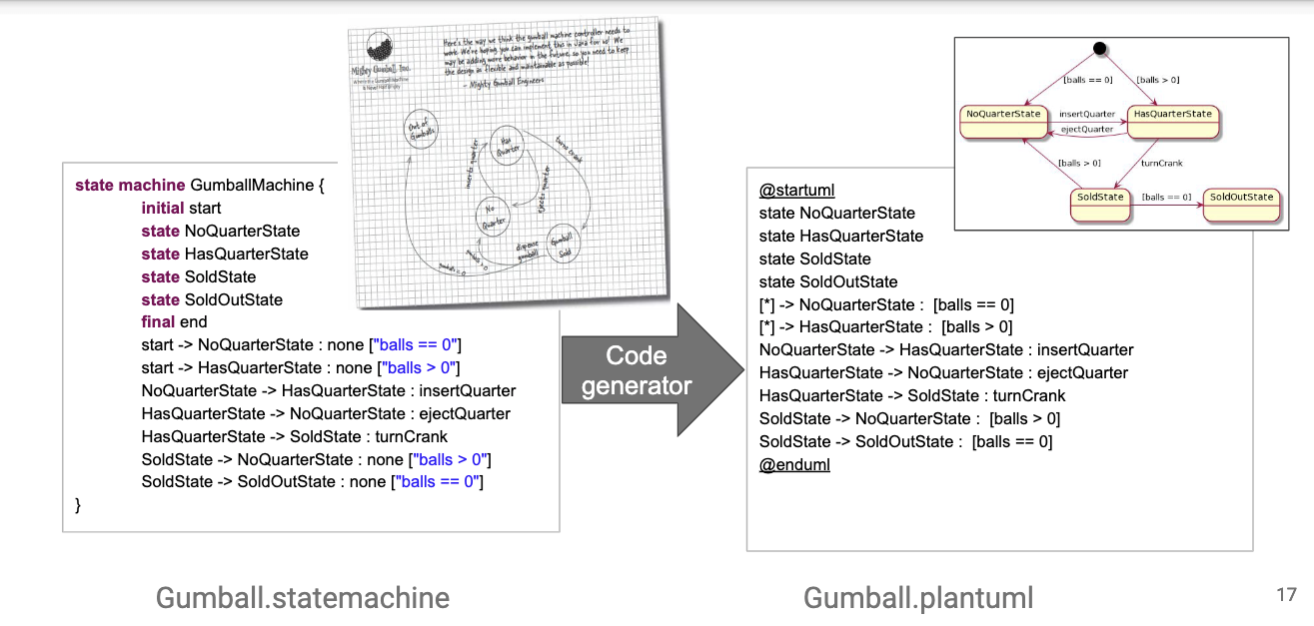
- lang defined using modeling framework
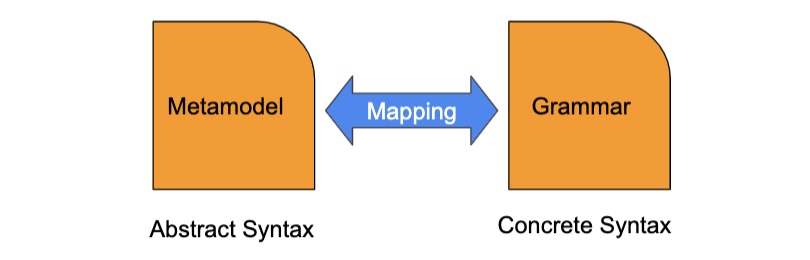
- abstract syntax - defined with class diag (metamodel)
- concrete syntax - defined with textual/visual grammar
- e.g., Xtext is a FOSS Java framework for defining textual modeling languages
- e.g., Statemachine lang
Xtext
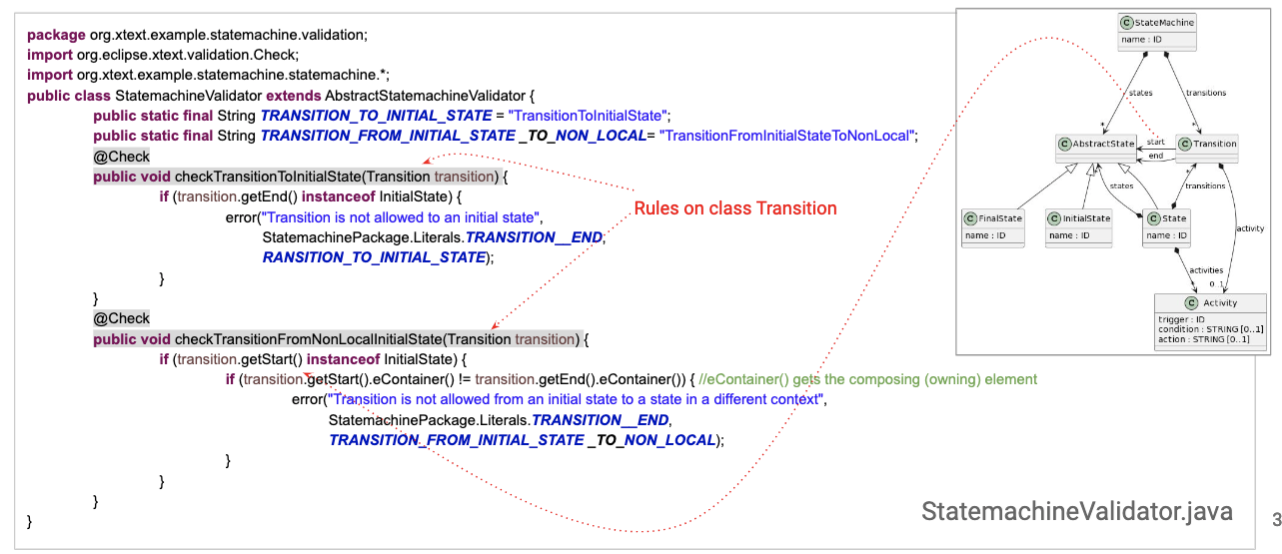
- xtext generates a Java API corresponding to the class diagram of the grammar
- xtext also generates a validator java class for the lang - each rule is decorated with
@checkwith a parameter of the las type