11 - Lighting
ucla | CS 174A | 2024-03-18 22:08
Table of Contents
Types of lighting
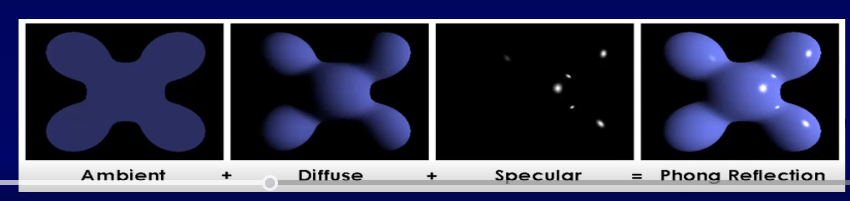
- ambient - instead of checking the physical scattering, we assume each object has ambient lighting directly behind it that gives us a silhoutte
- diffuse - reveals shape of obj based on diffusivity of light across the surface of the object
- specular - shine, shows specualr highlights of the light soruces
Ambient Lighting
- background light - estimates true scattering
- does NOT depend on position/direction, object, or eye

Diffuse Lighting
- point source light
- lambertian (diffuse) reflection for dull matte surfaces -> looks equally bright from all directions
- reflect light equally in all directions
- Lambert’s law: light intensity is prop to direction

- N is the normal from/to the surface
- L is the light vector (surface to light source)
Specular Lighting
- shiny surfaces
- color of light matters (included in point light intensity) not color of object
- depends on position of light, object and eye
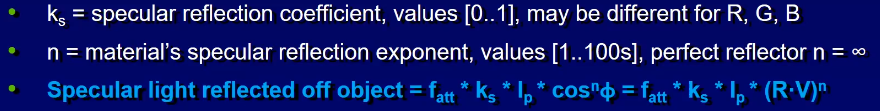
- R is the reflection vector from the surface
- V is the view/eye/cam vector from the surface
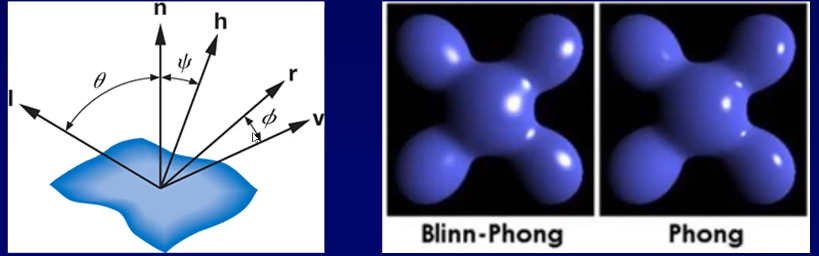
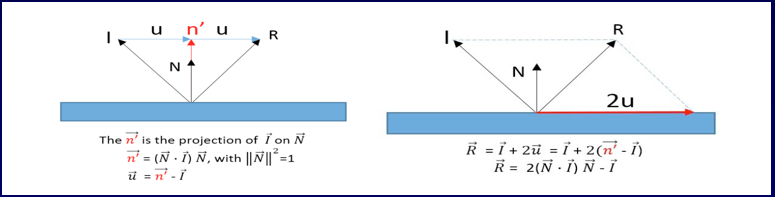
Calculating R vector
Blinn-Phong: Replacing RV with Halfway Vector
- halfway vector
- replace
- s.t.
Final Lighting

Incident Angle
- angle is angle bw norm to surface and light source
Directional light sources
- if light is far enough away
- L is the same (constant) for the entire scene for all objects
- N is the same for the entire polygon
- thus
Attenuated Light source
- diffuse light reflected off object
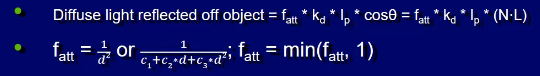
- d is the distance of the light to the object
Colored Light Sources
OBJECT COLOR (not light color)
- object’s diffuse color
- split into R,G,B components
- thus final term => (ambient + diffuse term) *
Fog: Atmospheric Attenuation and Blending
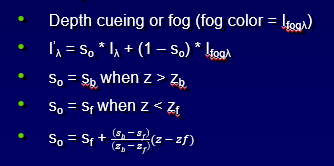
Misc Improvements

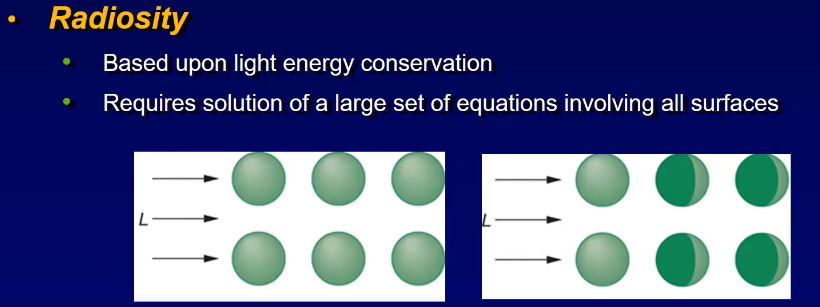
Global Illumination
- based on physics light energy (radiosity)