16 - Virtual Memory
ucla | CS M151B | 2024-03-05 17:17
Table of Contents
Background
- modern apps are multi-program
- each program need to think it has its own heap:
- naive approach - static paritioning
Static Paritioning

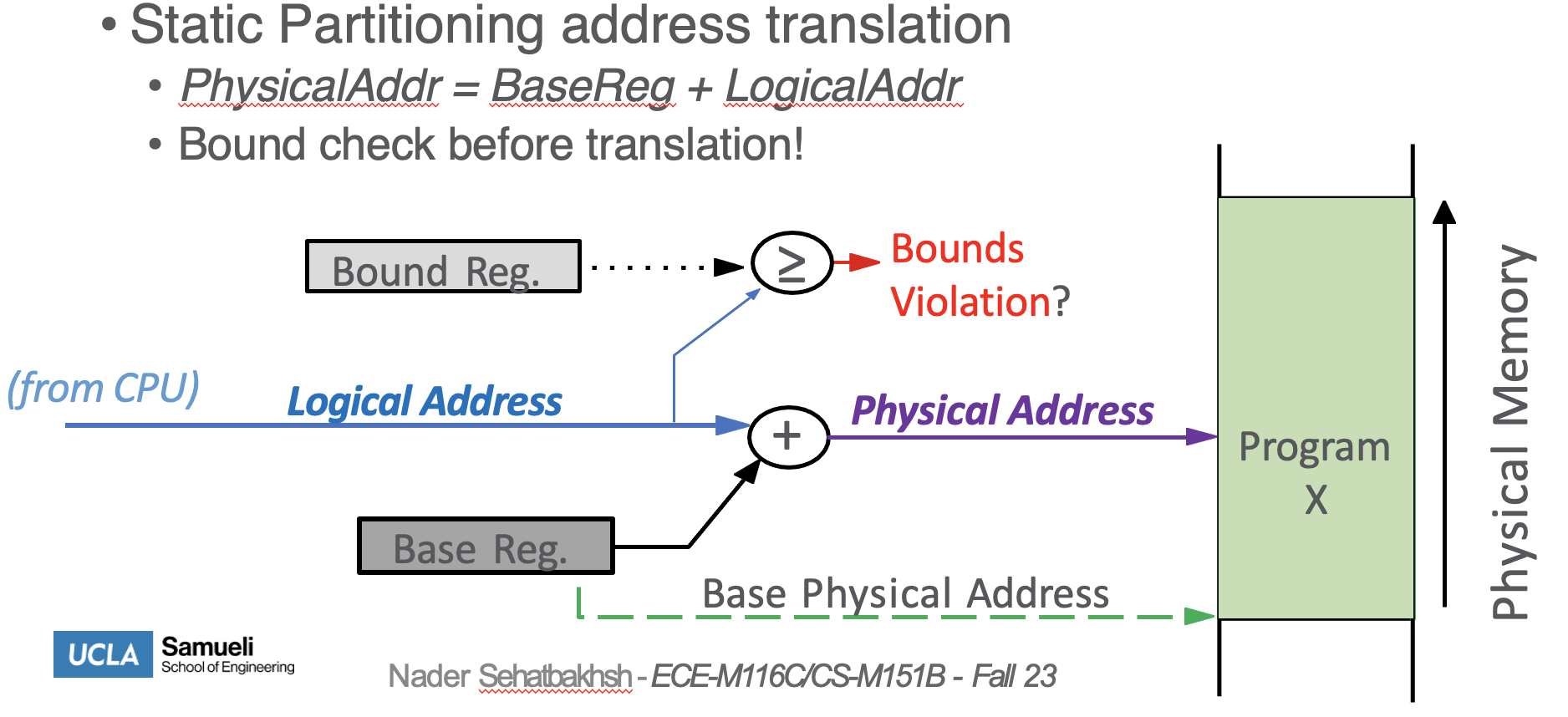
- balance check and give each program a static address space called “logical addres”
- then have a base and bound
- we can check bound with just the logical addresses
- then to allocate on physical address space - add base + logical address
- issue - not all program need the same amount of memory
Virtual Memory - Dynamic Partitioning
- allocate a page file for each program on physical memory- fixed size
- then each program’s virtual (logical) address space is the full address space or more (usually more) but when allocating new memory, it has access to the page file on physical memory
- if a program needs more than its 1 page file (page fault), OS allocates a new page file where free in physical memory and assume it continuous to the program’s virtual (logical) addresses
Address Translation
virtual address: $$\text{[ virtual page number (VPN) page offset ]}$$ physical address: $$\text{[ physical page number (PPN) page offset ]}$$ - then only do address translation between VPN <-> PPN
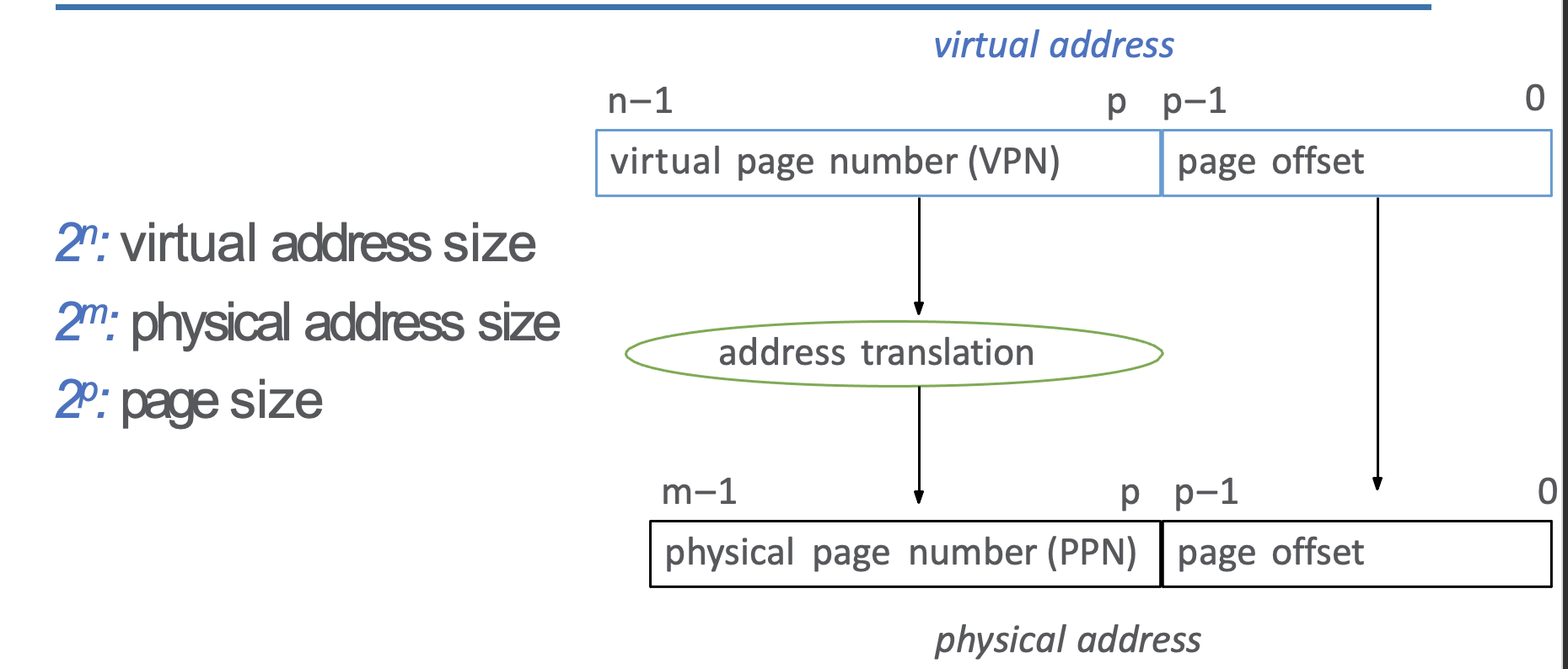
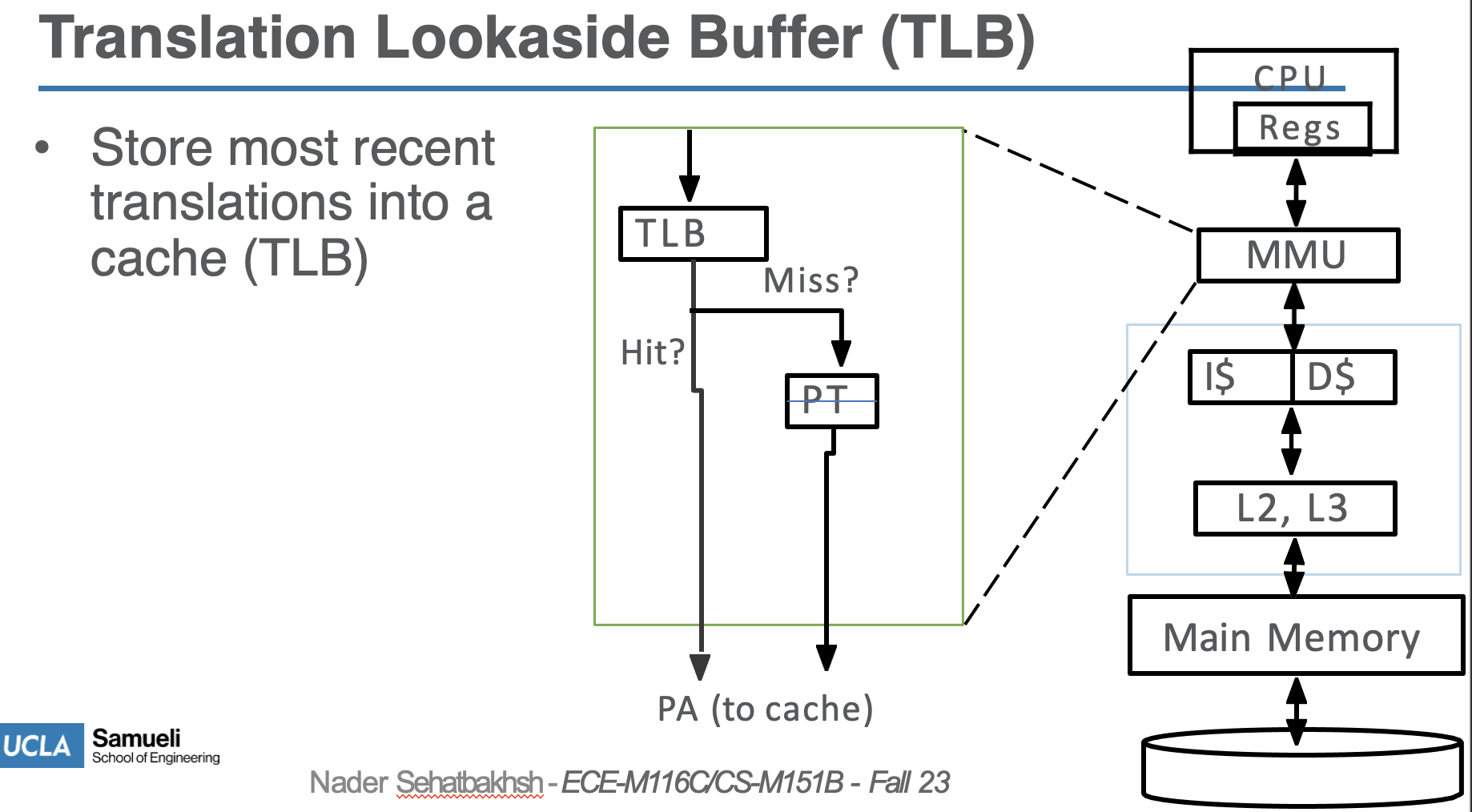
- address translation is usually a lookup table in Page Table with VPN as index
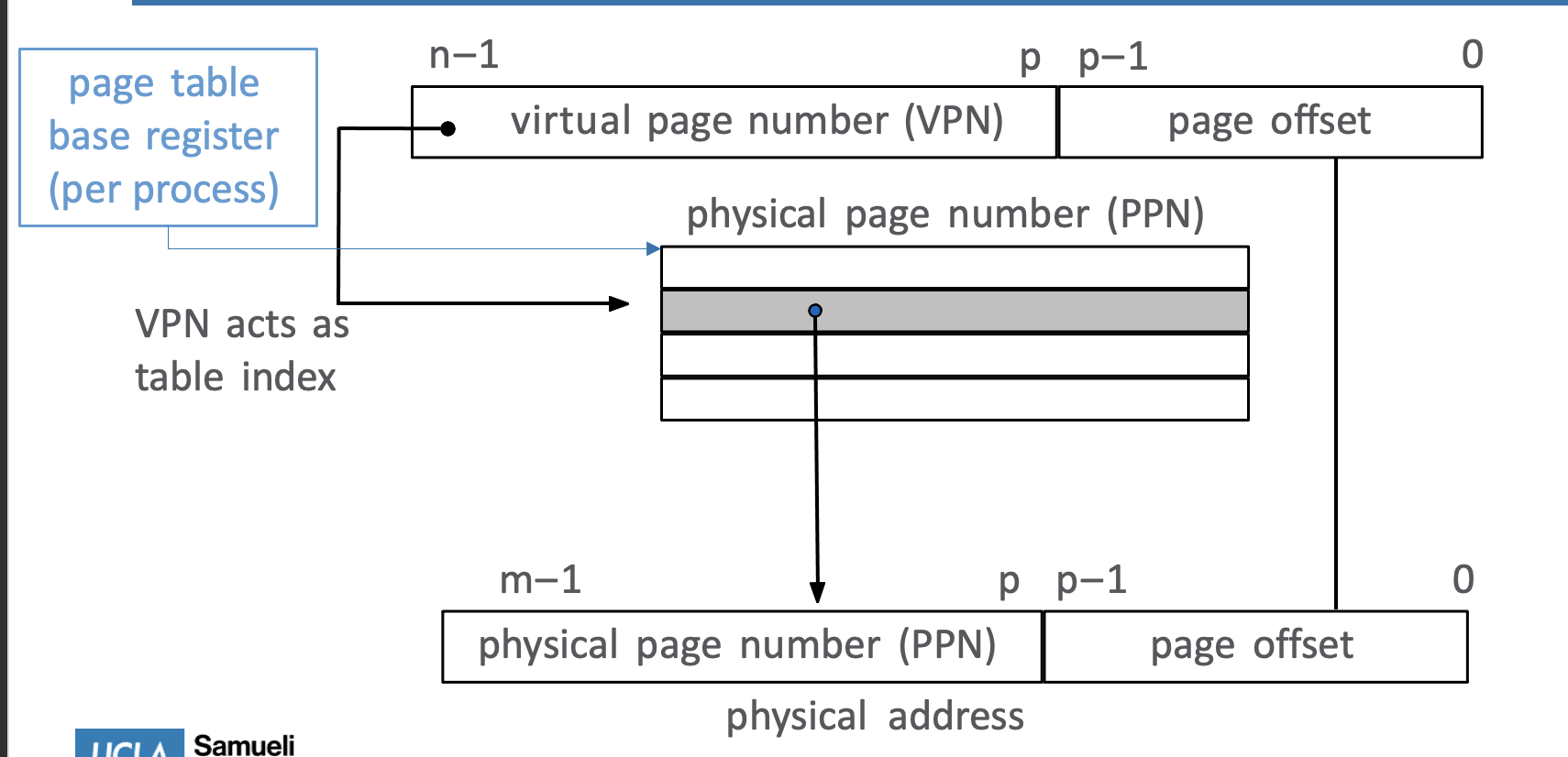
- each program has its own page table, and the OS will deal with context switching by indexing into that program’s page table using MMU (done using CSRs in RISC-V)
Example
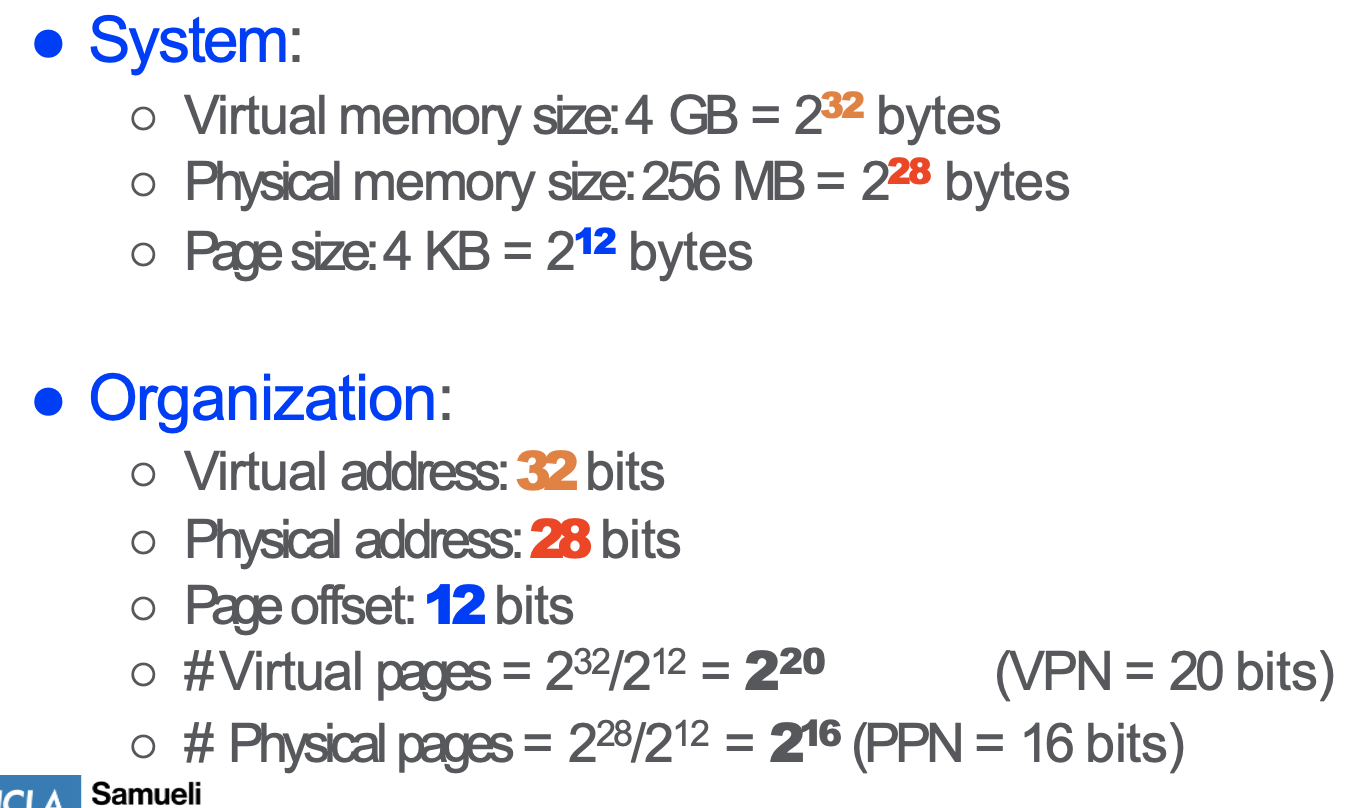
Page Table
PTEs have flags (tags) alongside the PPN:
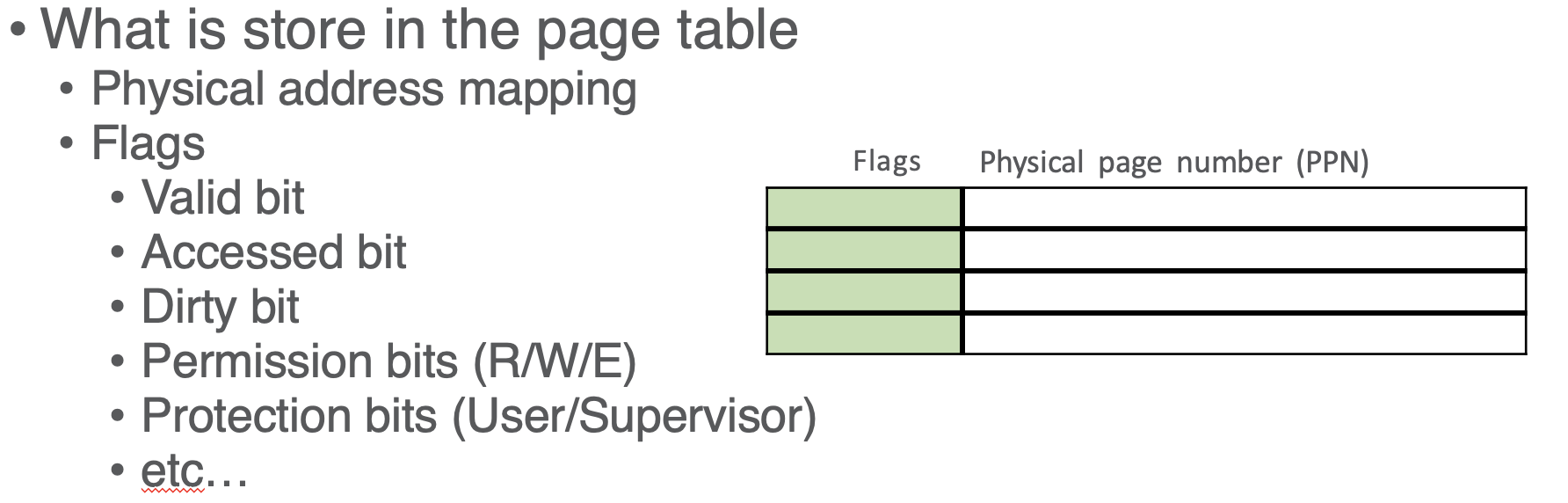
- page tables also have a base register to indicate the starting address of the physical page table in the physical memory, so pulling a page is done in 2 steps:

Page table size calc

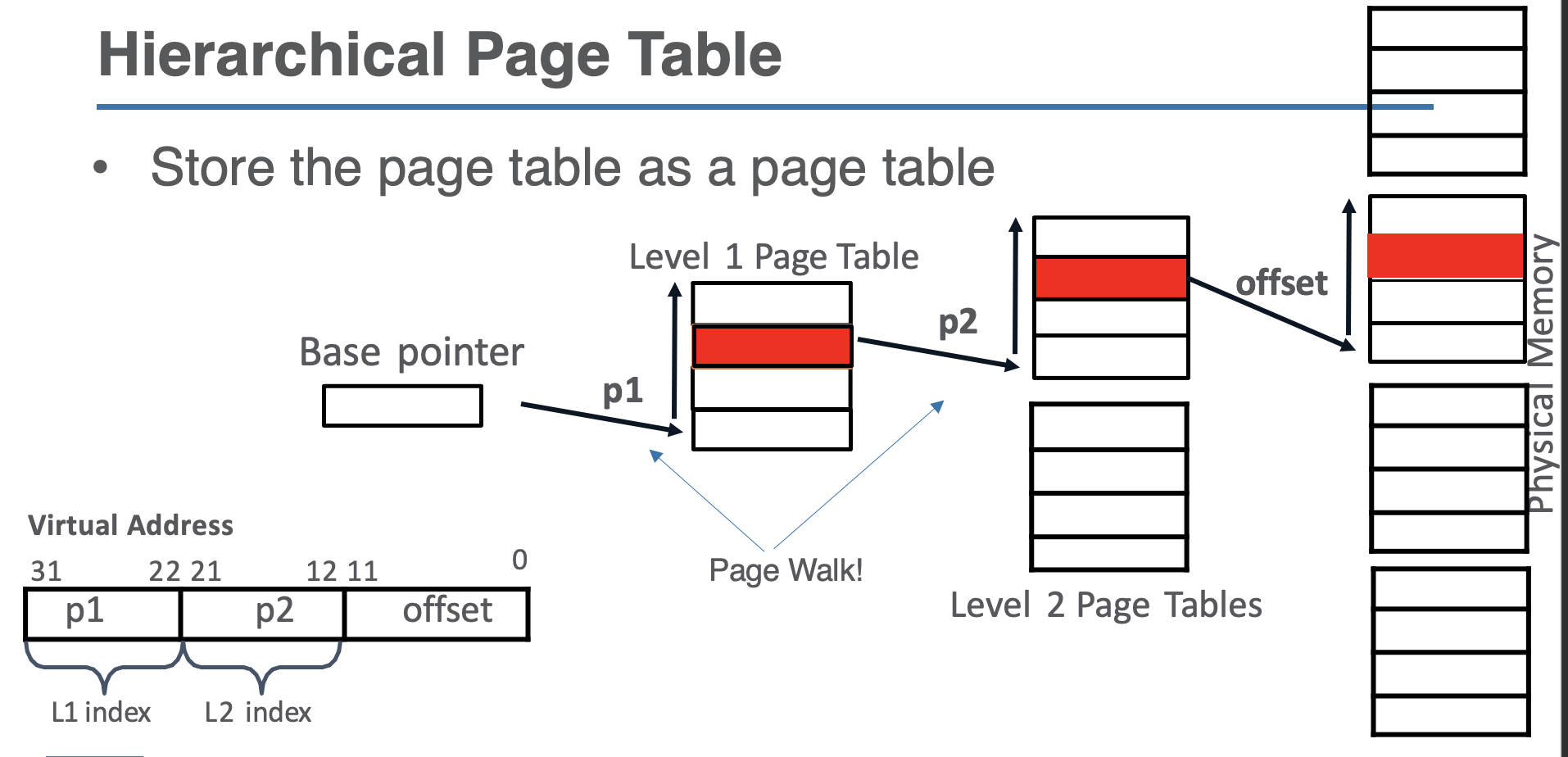
Hierarchical Page Table