03 - Unified Modeling Language
ucla | CS 130 | 2024-10-07 18:37
Table of Contents
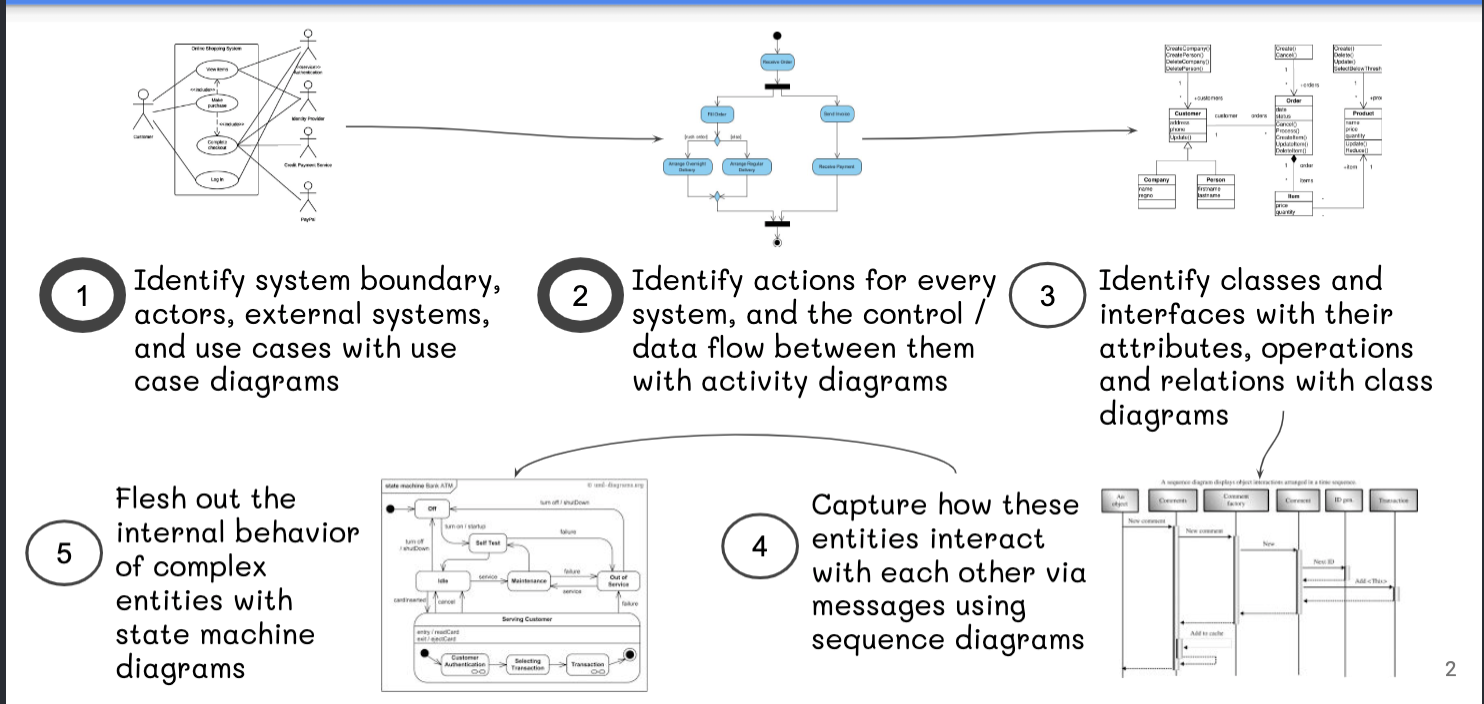
Unified Modeling Language (UML)
- older, more popular framework for designing diagrams
- allows for multiple analysis methods
Use Case Diagram
- describes system as aa black box, used to model the customer interaction
- identifies possible service use cases, actors/interfacers, external system interactions
- e.g.
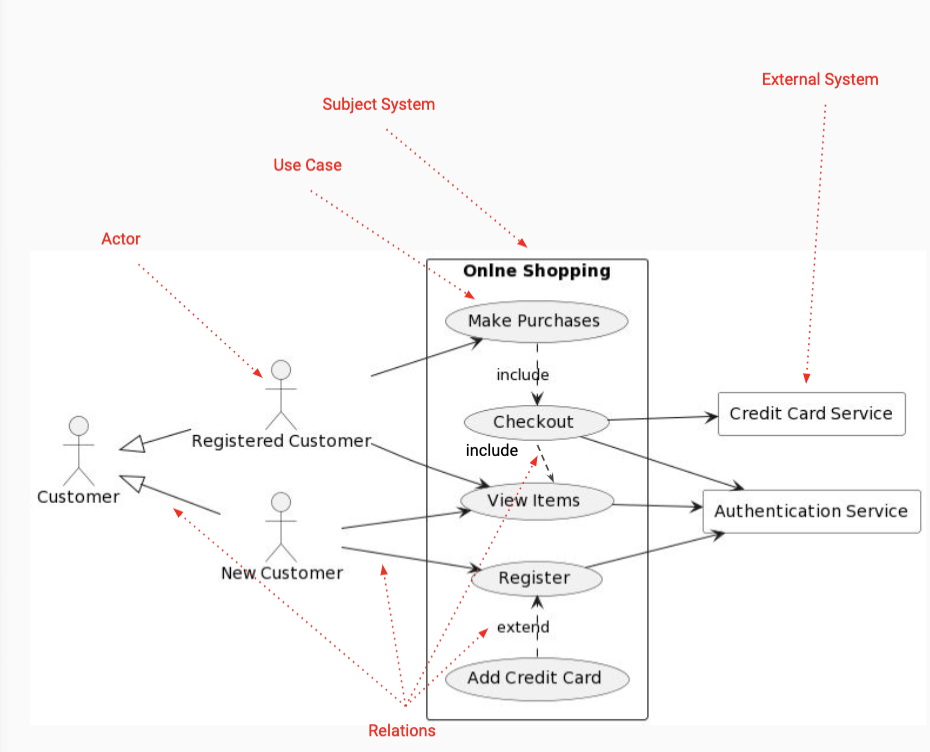
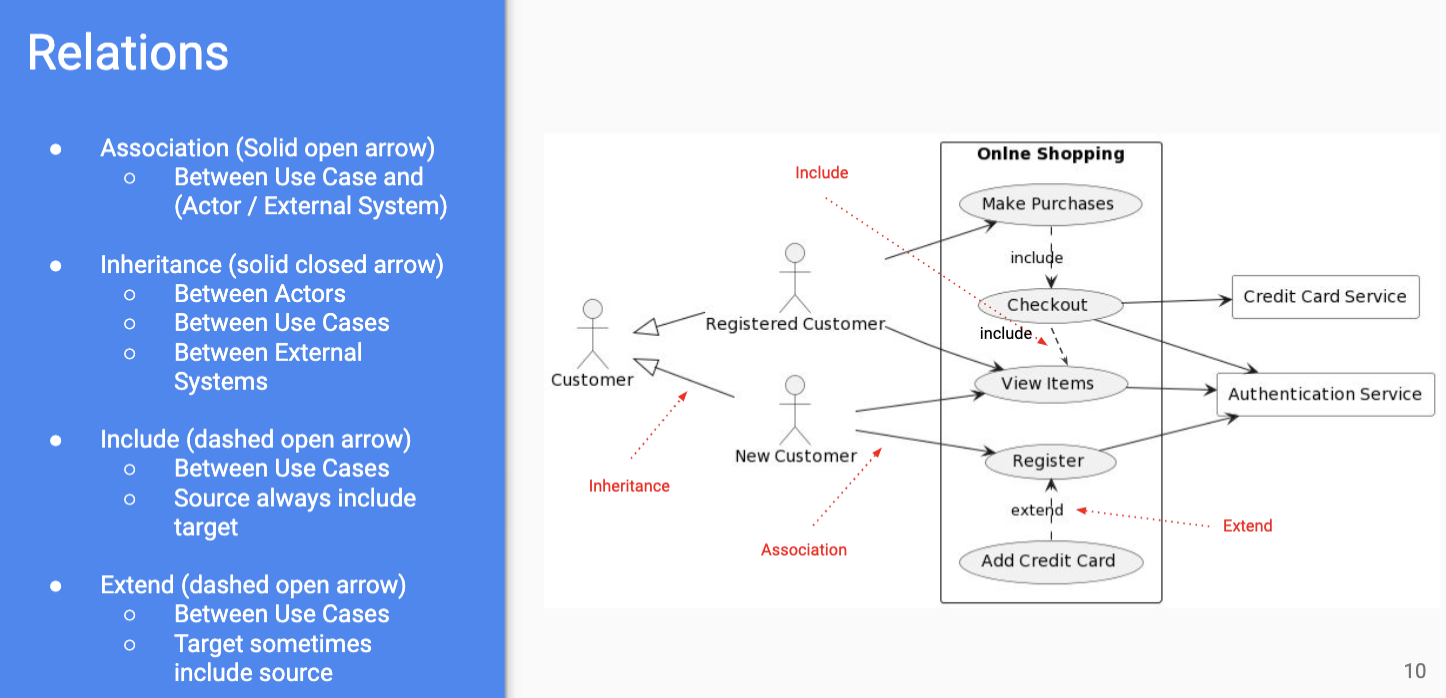
- relationships between actors/interactions
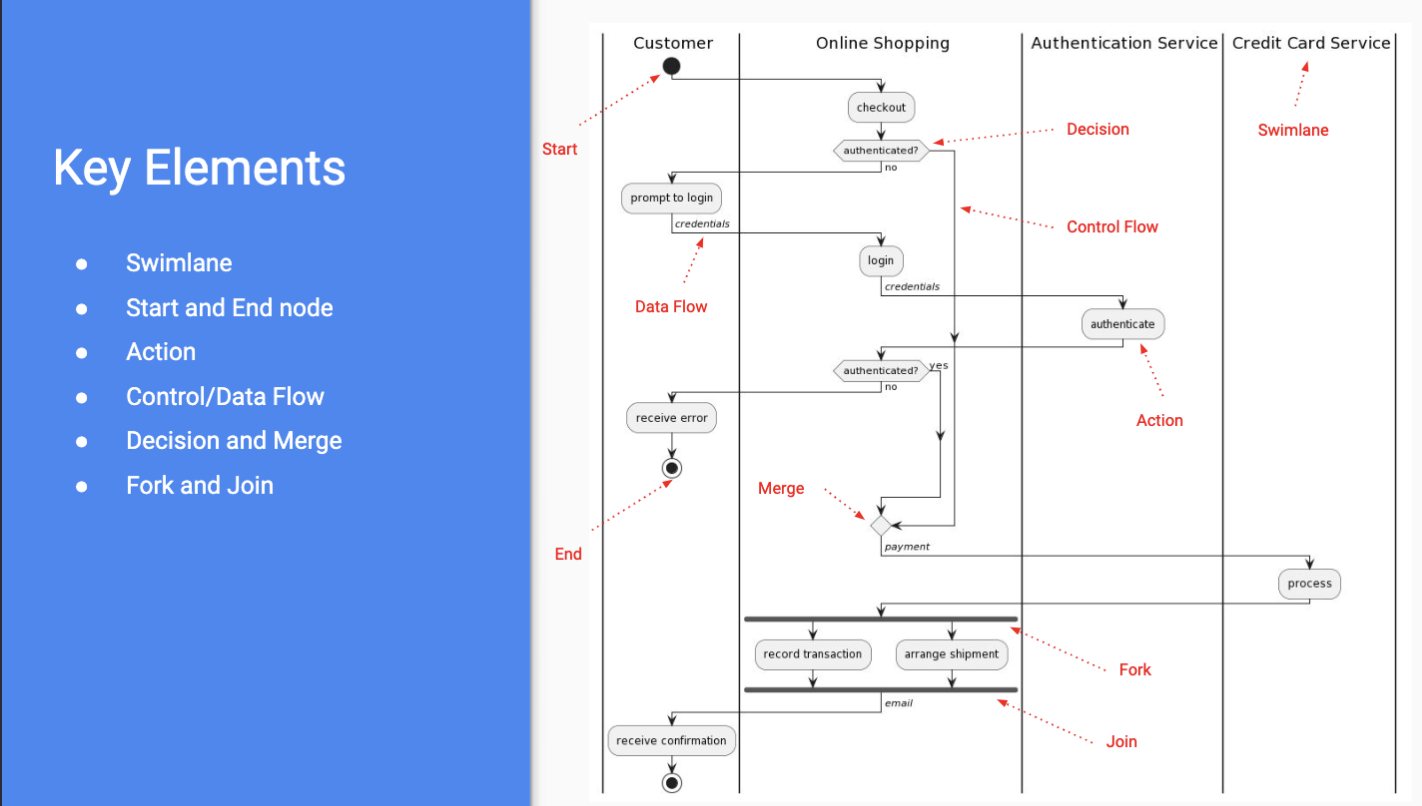
Activity Diagram
- models control flow and data flow in a use case of the subject system
Class Diagram
- describes white boc implementation of a system in terms of types: classes, interfaces, primitives
- a type defined by attributes and features/operations
- multiple abstraction levels
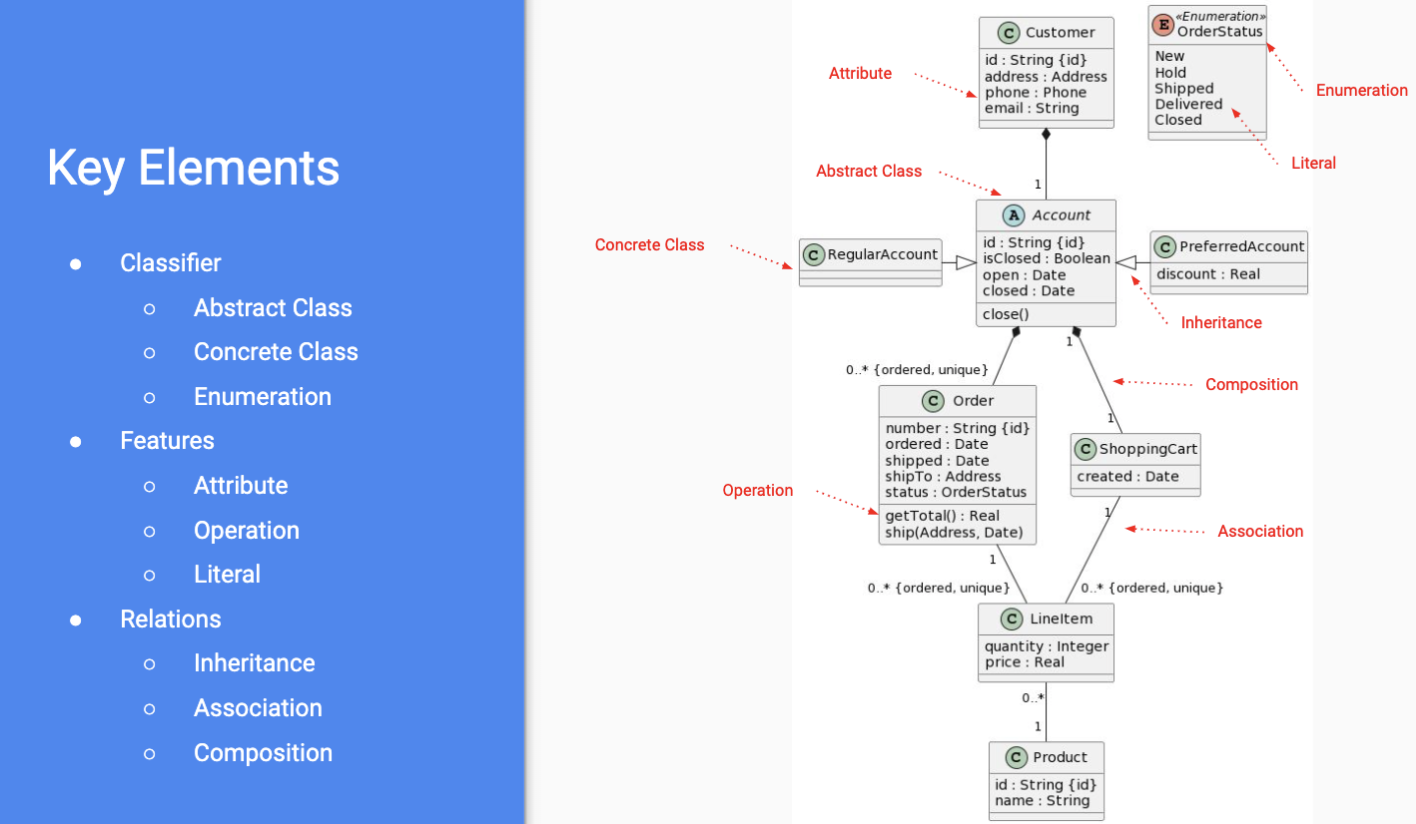
- abstract class - cannot be instantiated in italic
- integers on associations depict the possible count of the associated class within the higher up - there may also be “flags” that identify properties of the association NOTE: my descriptions of compositions uses terms source (arrow or empty end) and destination (diamond end); this conflicts with my description of association having source ()
- associations are directional - no arrows = bidirectionl, arrows represent that the source has a property of the dest. of the association arrow, but the dest. class has no property of the source class
- composition - association with a black diamond end (signifies special deletion semantics) = class by the diamond (destination) is an owner of the source, e.g. account is composed of 1 shopping cart
- important for deletions - items that are composed in another class will be deleted when the destination (black diamond class) is deleted
- deletion is transitive and cascades down composition connections but not association connections, deletion only cascades FROM diamond TO empty i.e., source only deleted if dest deleted in composition
- attribute/operation scoping
- : public; - : private; # : protected
- Attribute modifiers/syntax
- Operation modifiers/syntax -
 NOTE: from below i refer to diamond end as source and arrow end as destination
NOTE: from below i refer to diamond end as source and arrow end as destination - inheritance = source “is-a” dest;
- association/composition = source “has-a”
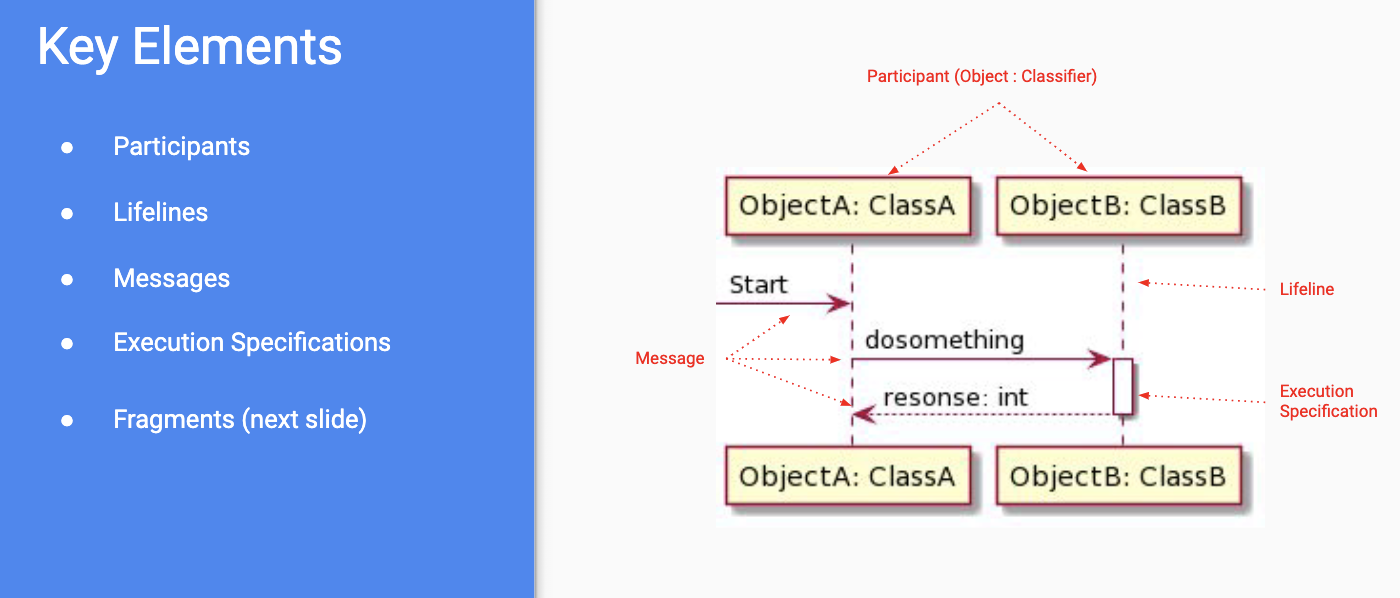
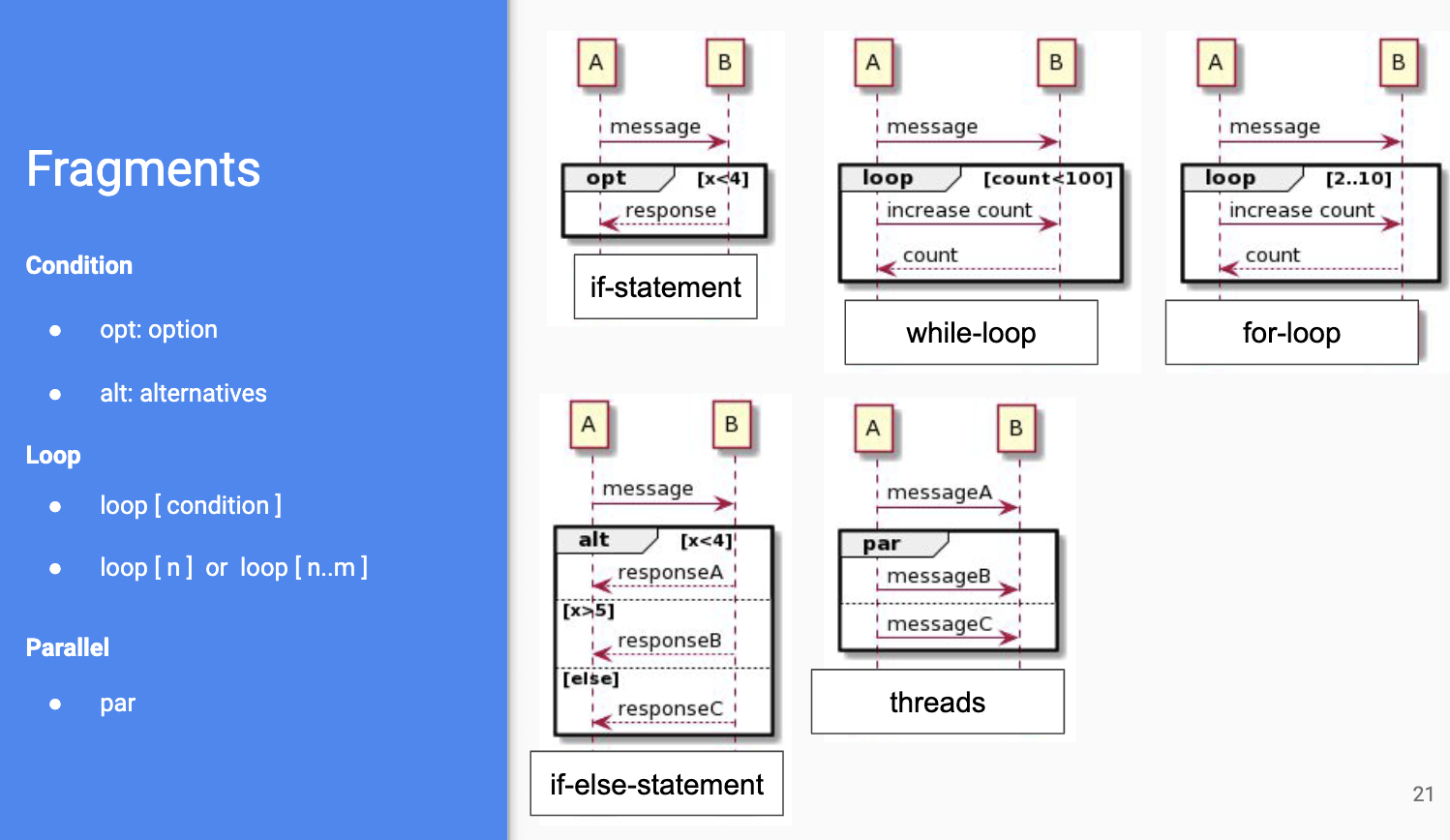
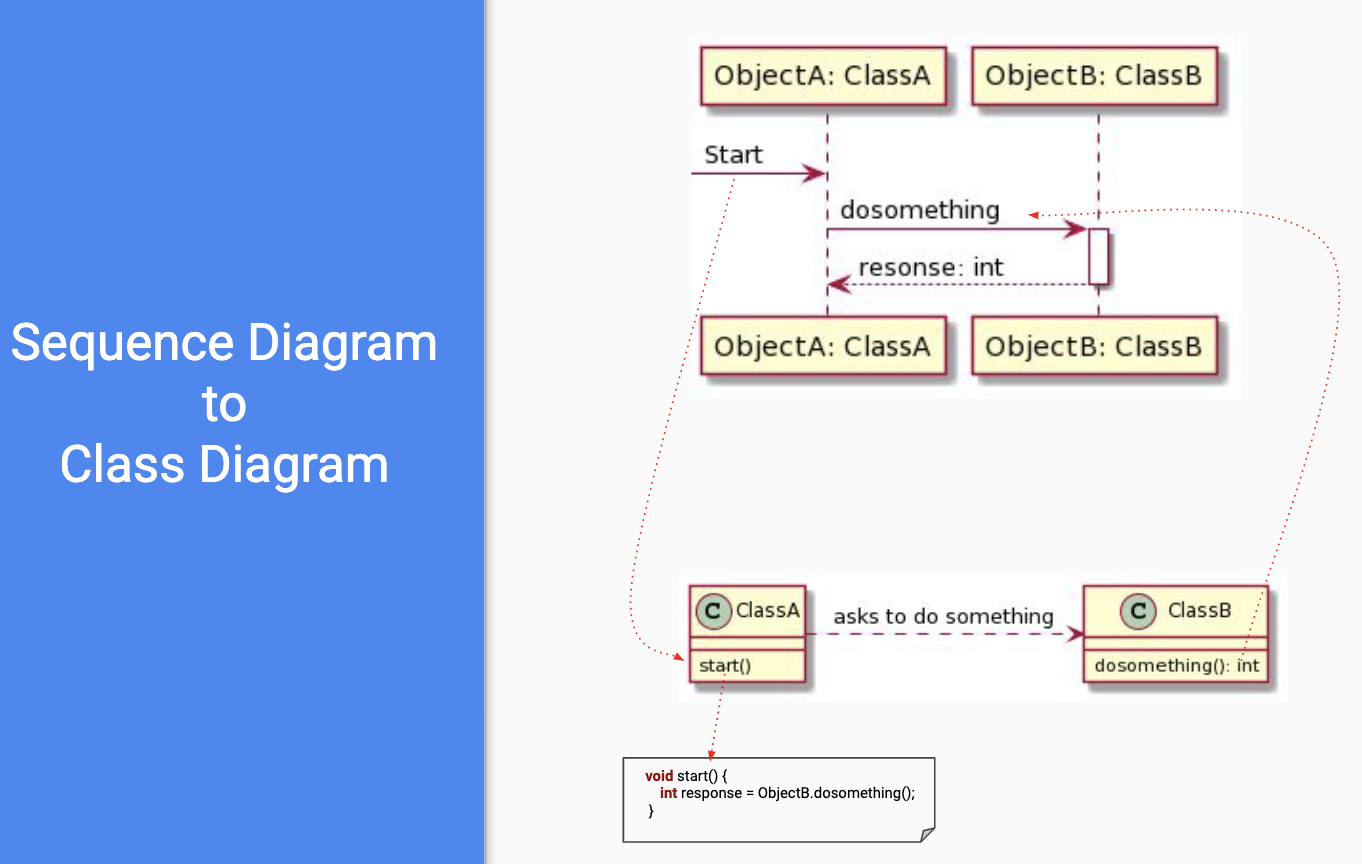
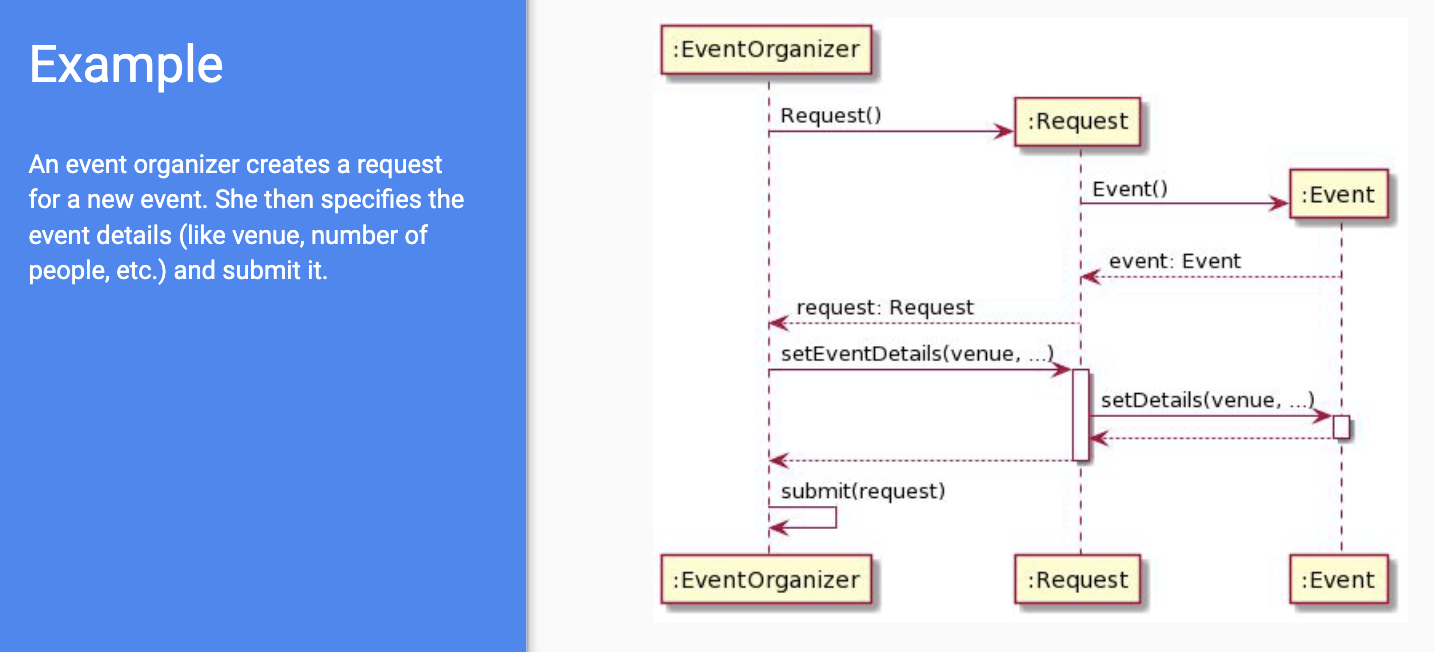
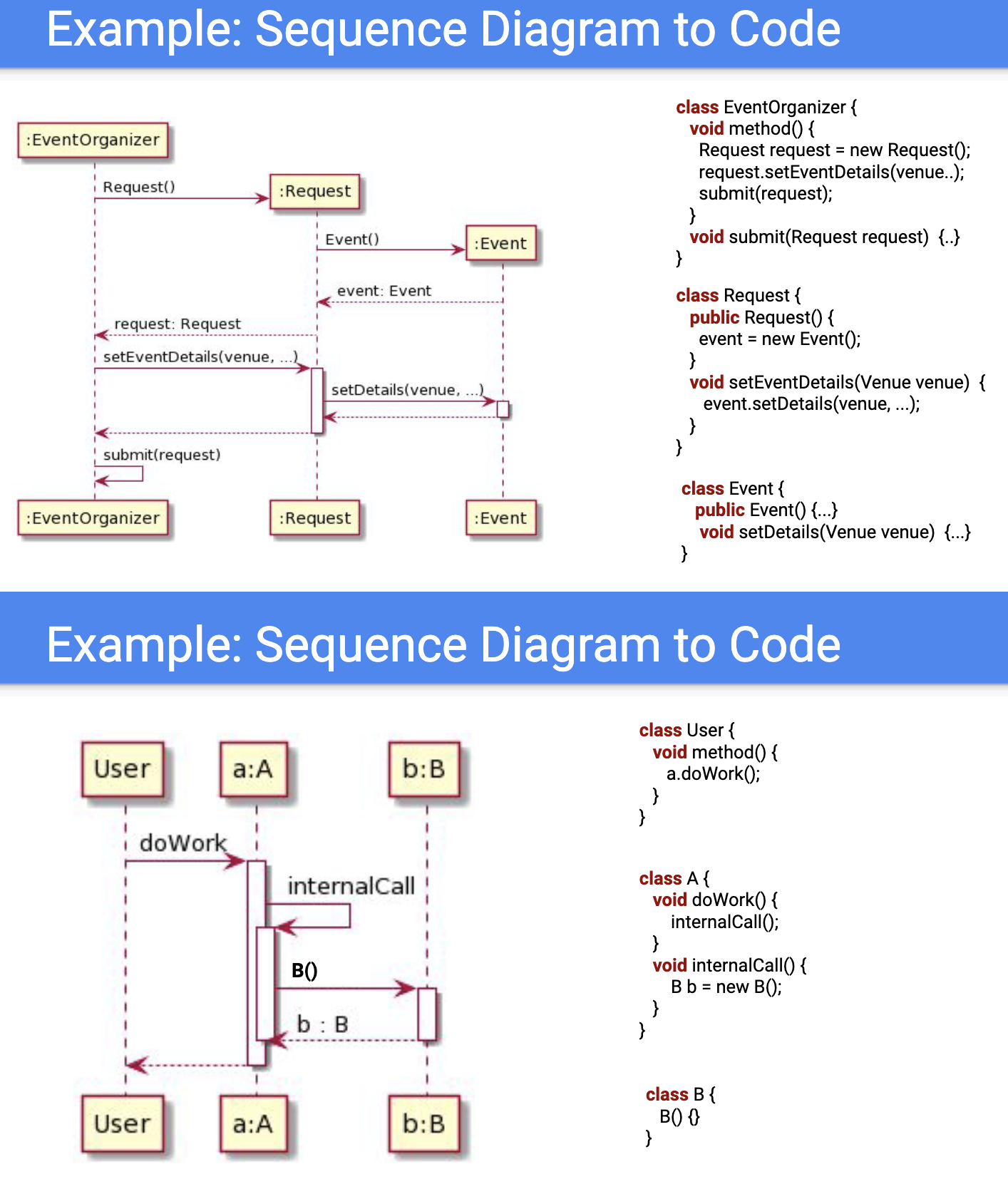
Sequence Diagram
- describes interactions in/between a system
- shown as exchange of messages; messages ordered in time (flowing downward)
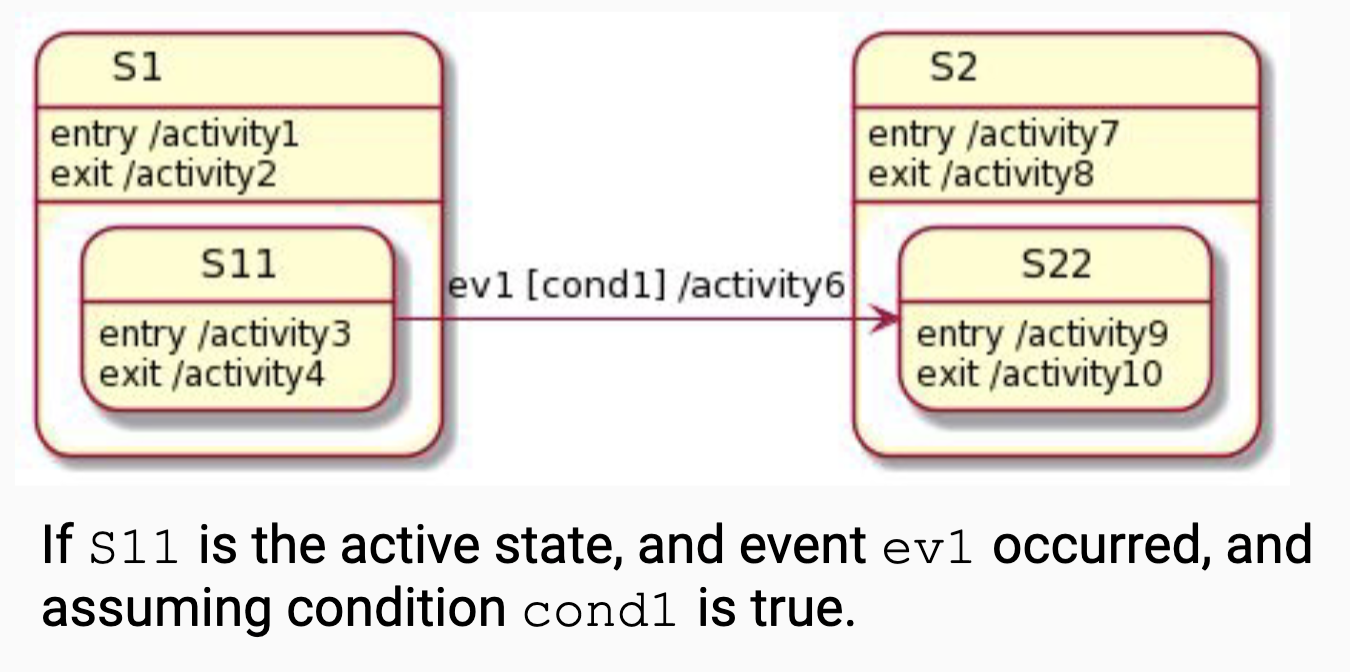
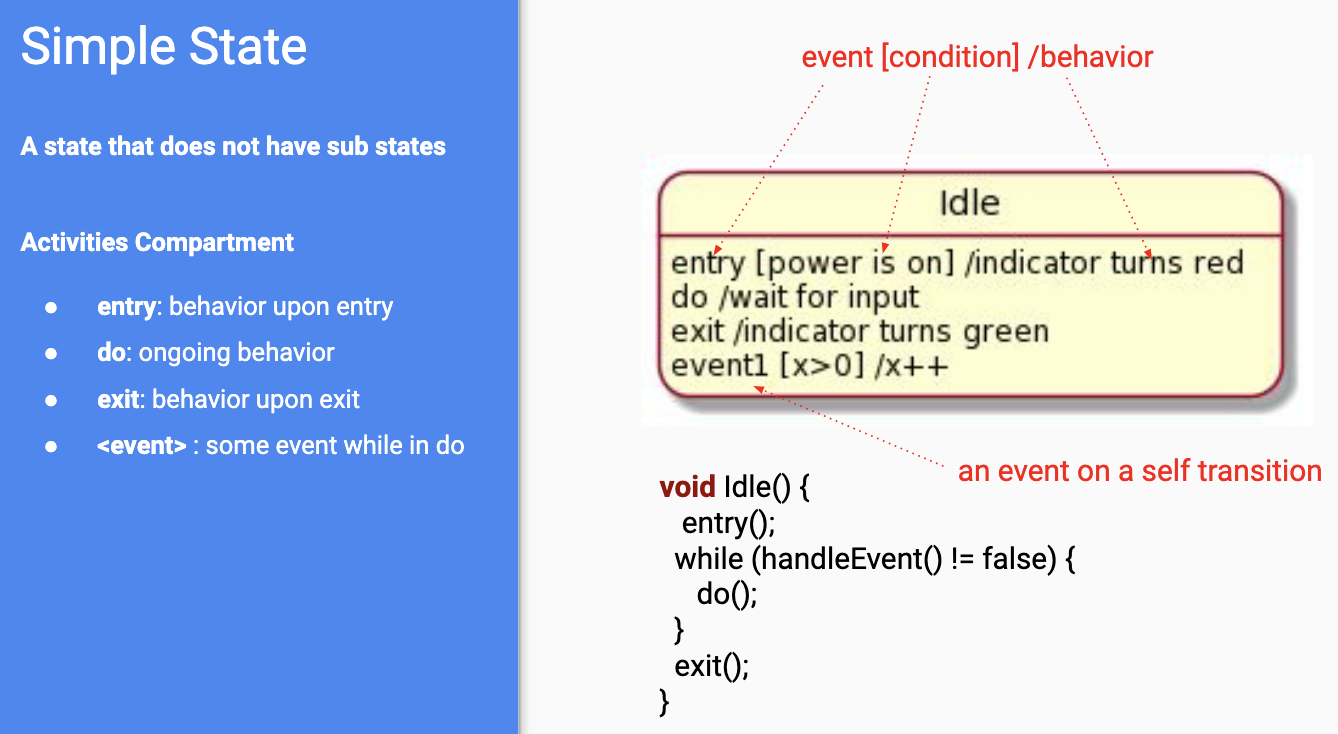
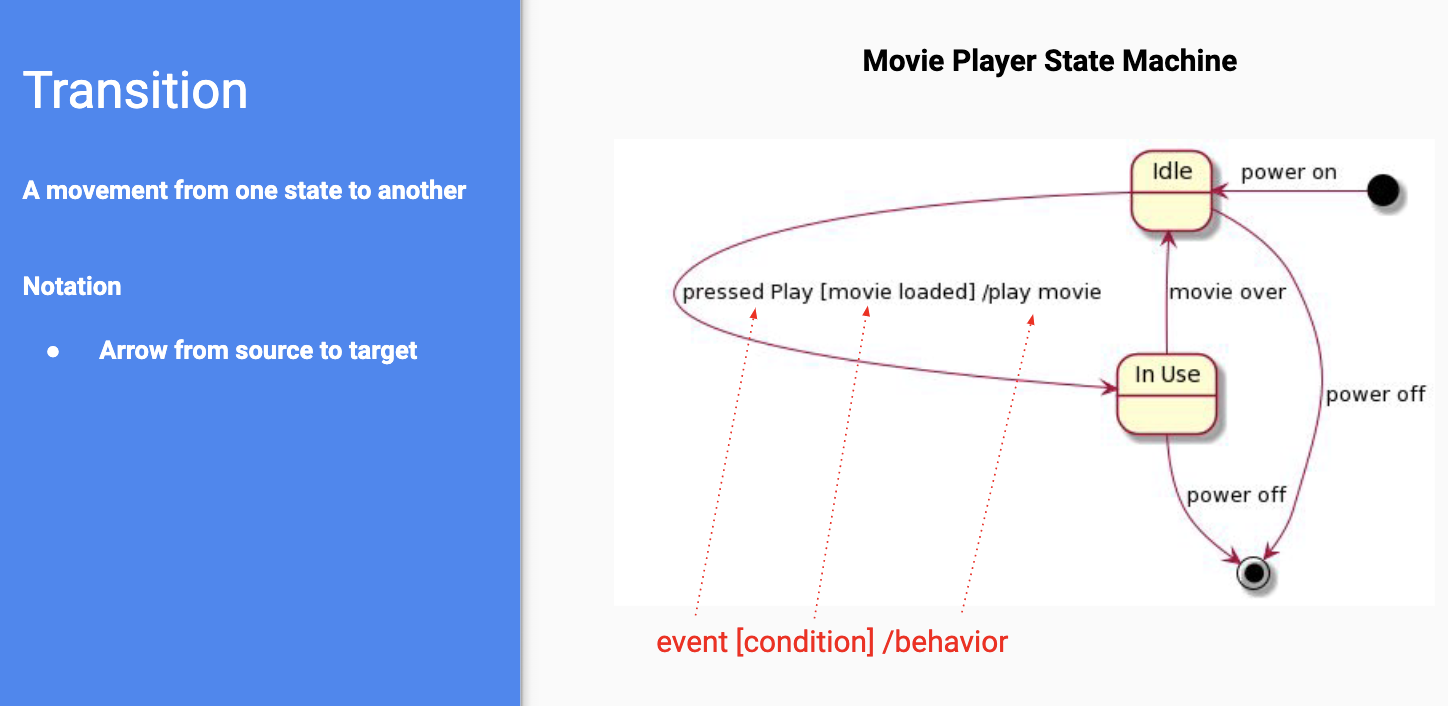
State Machine Diagram
- decribes states and transitions within a system or class
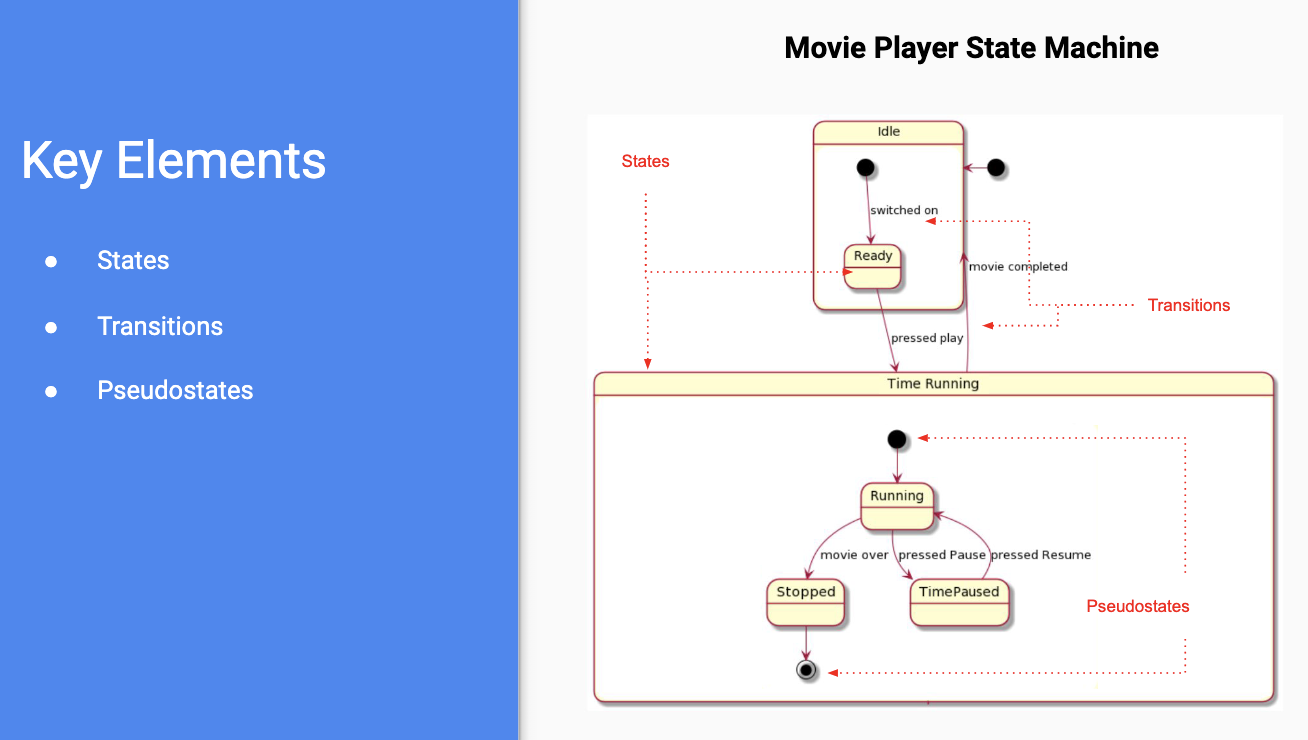
- a state can be simple or composite
- pseudo-states: entry exit - black dots, exit is circled
- e.g., activity4 -> activity2 -> activity6 -> activity7 -> activity9