04 - Software Architecture
ucla | CS 130 | 2024-10-14 18:11
Table of Contents
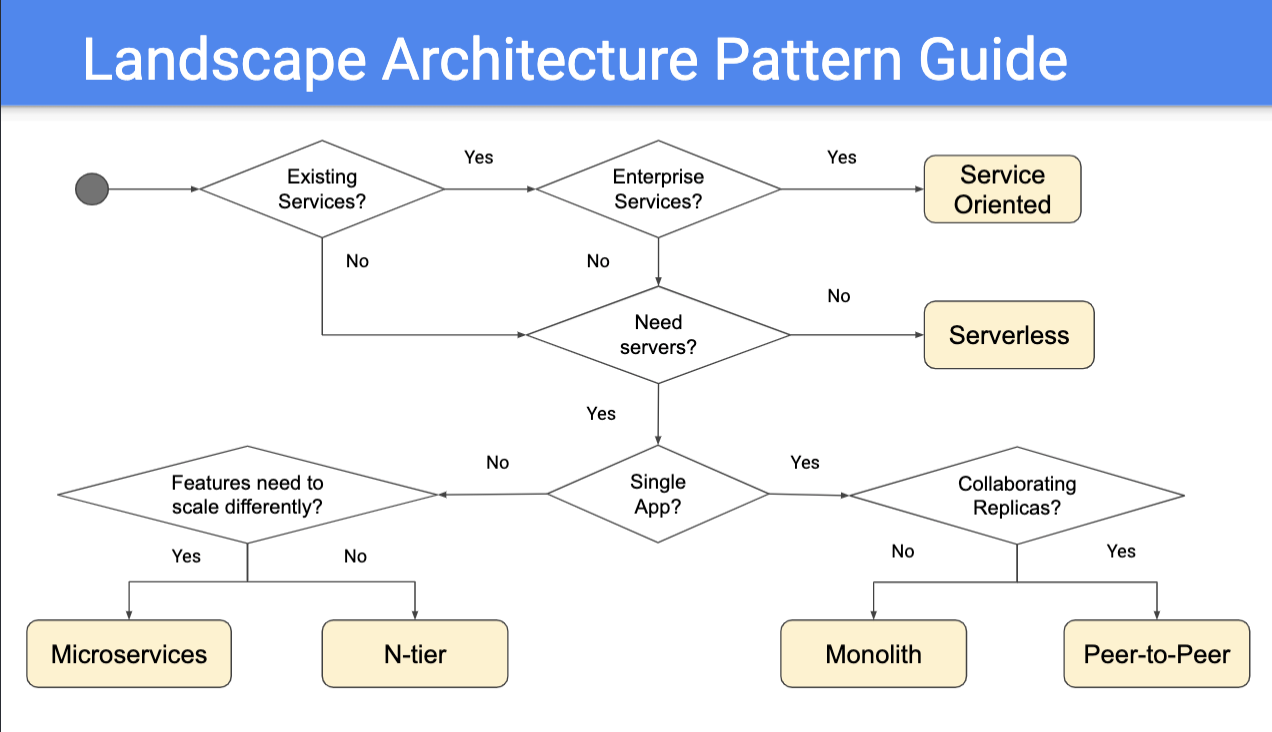
Application Landscape Patterns
- Monolithic
- Microservice -> each service (possibly multiple per layer) divided
- Serverless
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) -> user posted, user-guided, decentralized like crypto
Application Structure Patterns
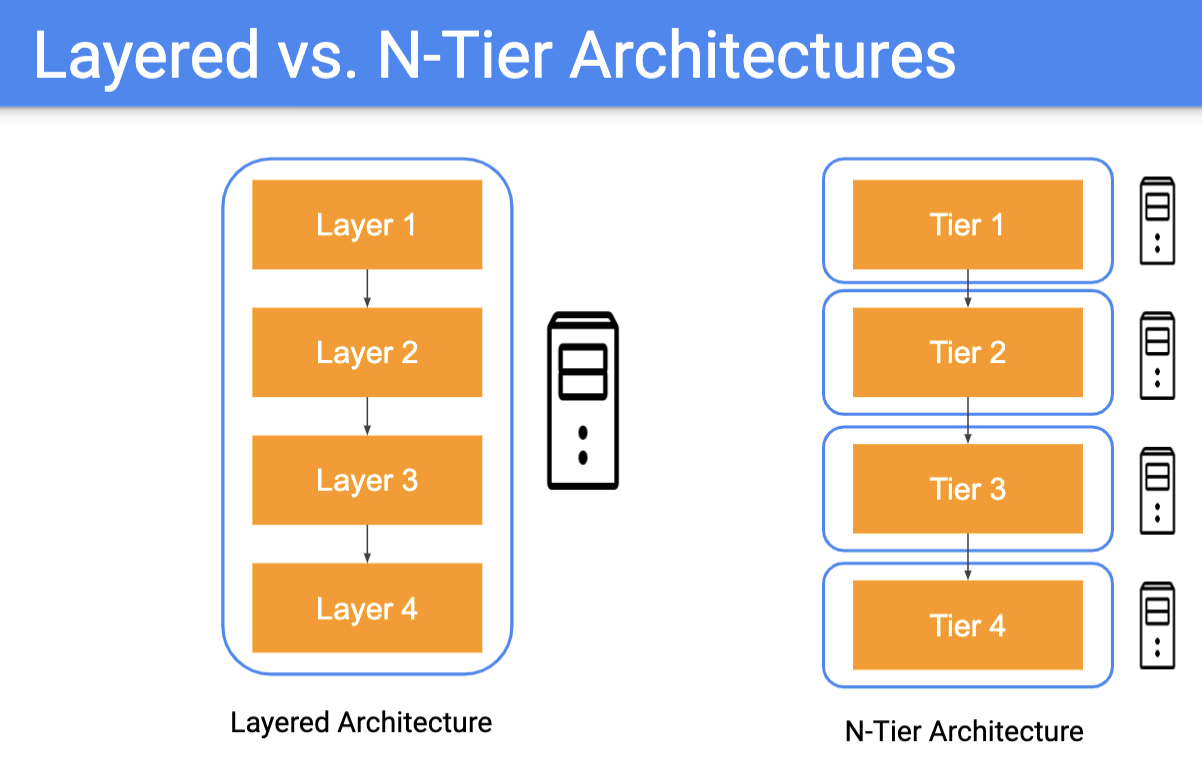
Layered Architecture
- separation at features/visibility

- pros: well known, separation of concerns
- cons: can lead to monoliths, need to write lot of code bw layer, sinkhole anti-pattern
Microkernel Architecture
- plugin based
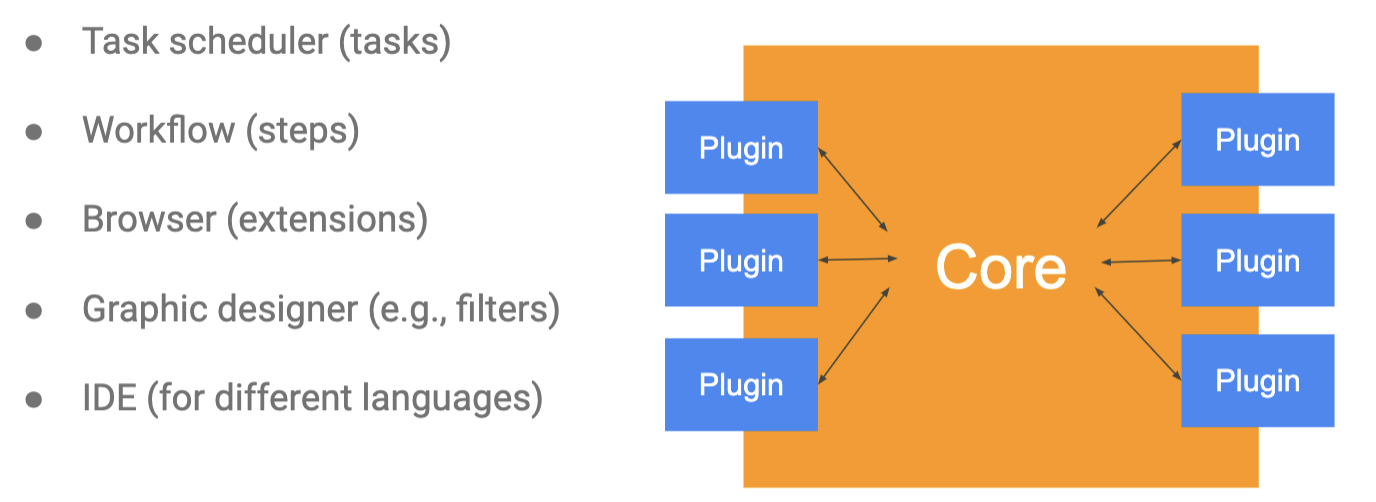
- e.g., IDEs
- pros: flexibility, clean separation of feats and teams, modify functionality at runtime
- cons: core api versioning challenges, untrusted plugins, plugin vs core decisions confusing
CQRS Arch (Command Query Responsibility Segregation)
- feat separated stacks, synced in back
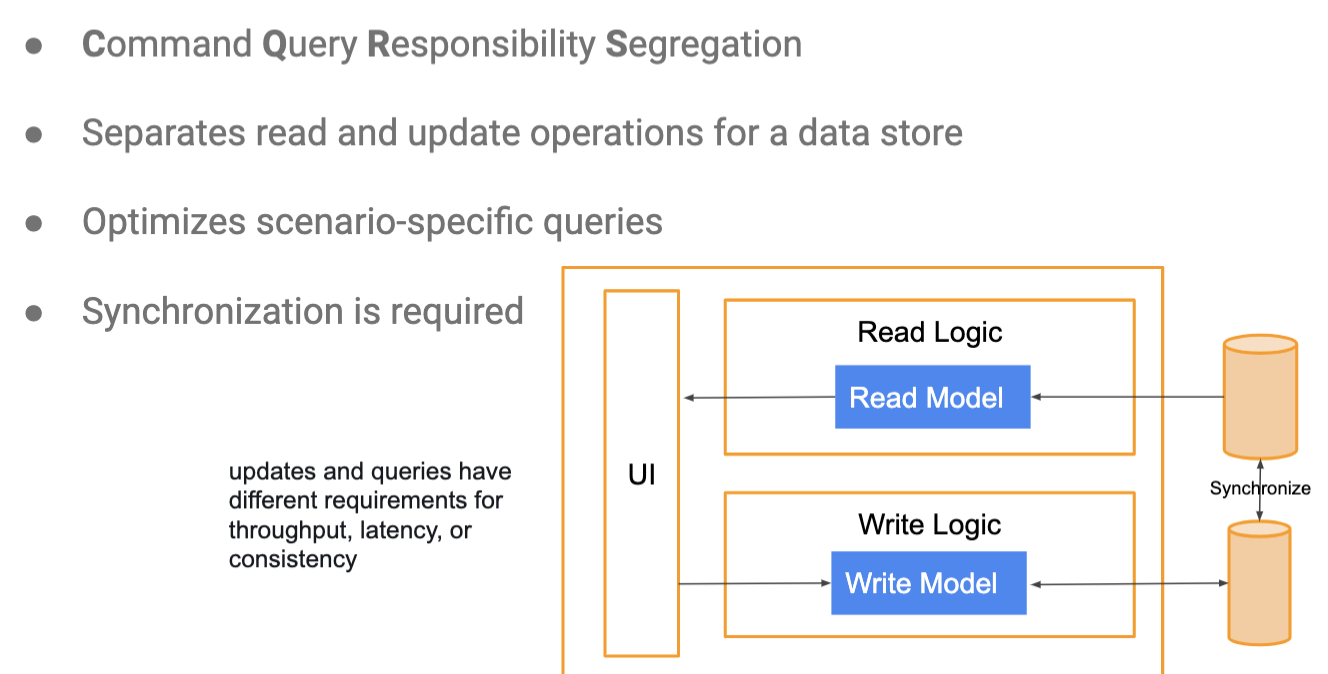
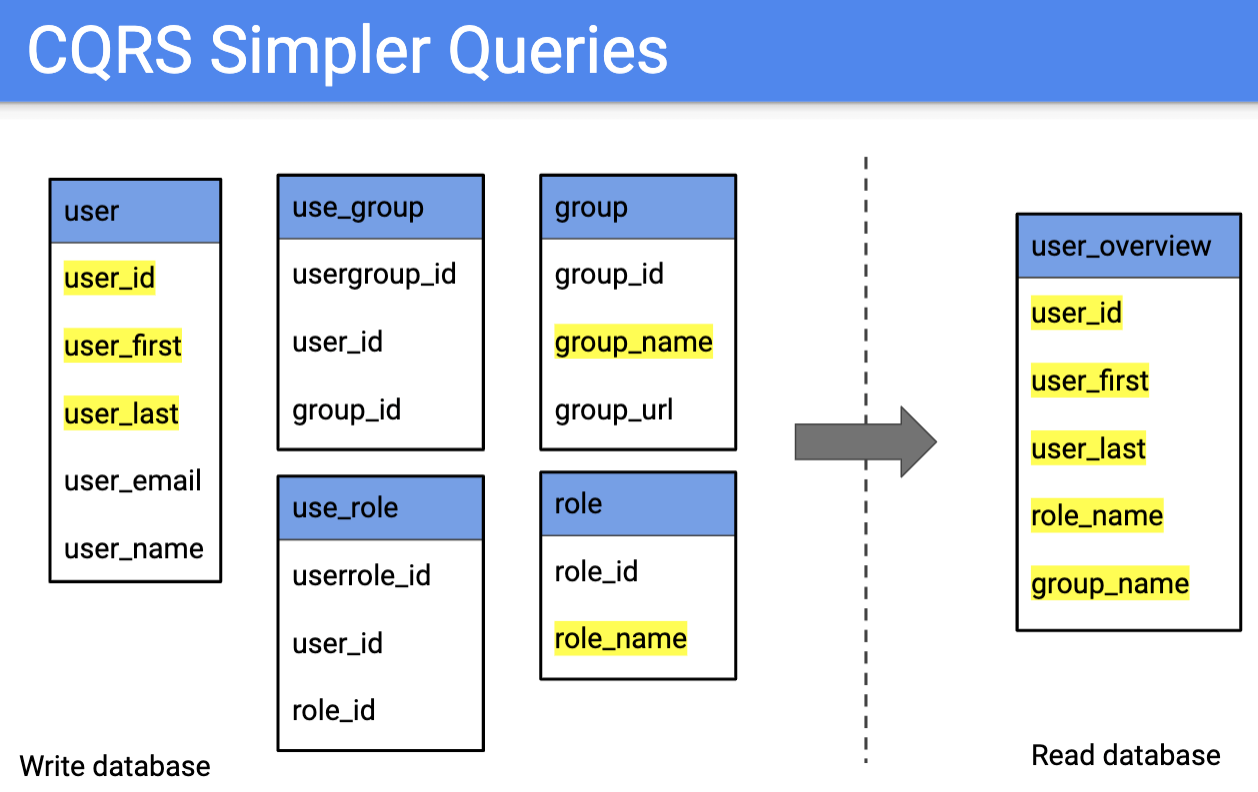
- e.g., banking apps - imbalance in read to write request usage
- pros: simple/fast/scalable reads
- cons: more complex impl. and learning, data and eventual inconsistency due to syncing
Event Sourcing Arch
- action based - store actions s.t. state is the result of the last stored action
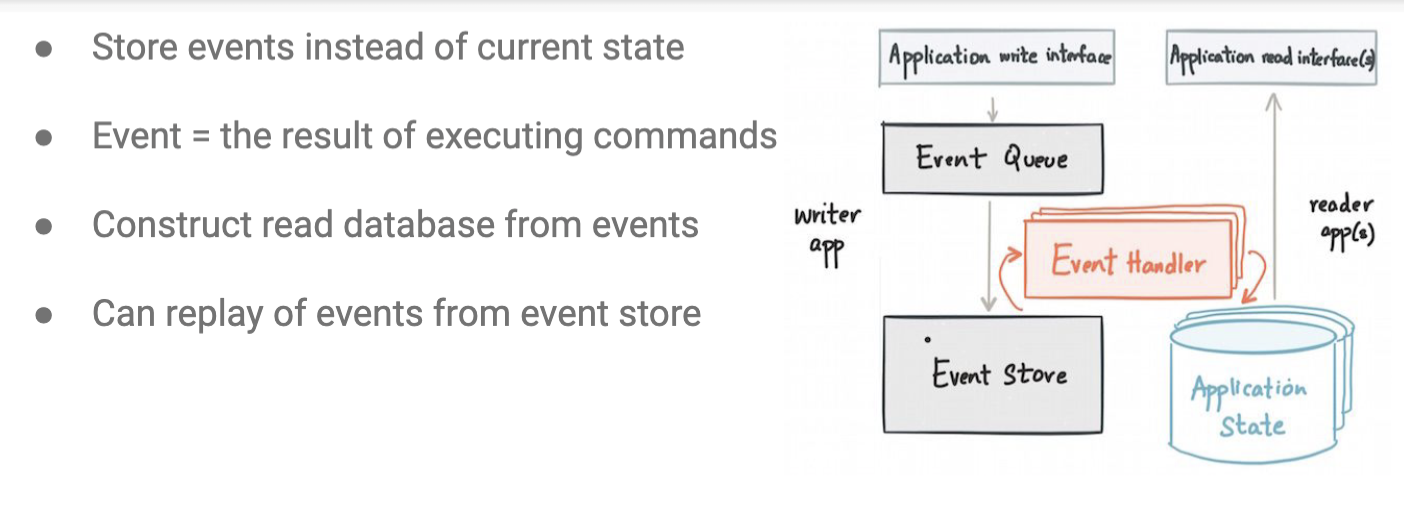
- e.g., netflix
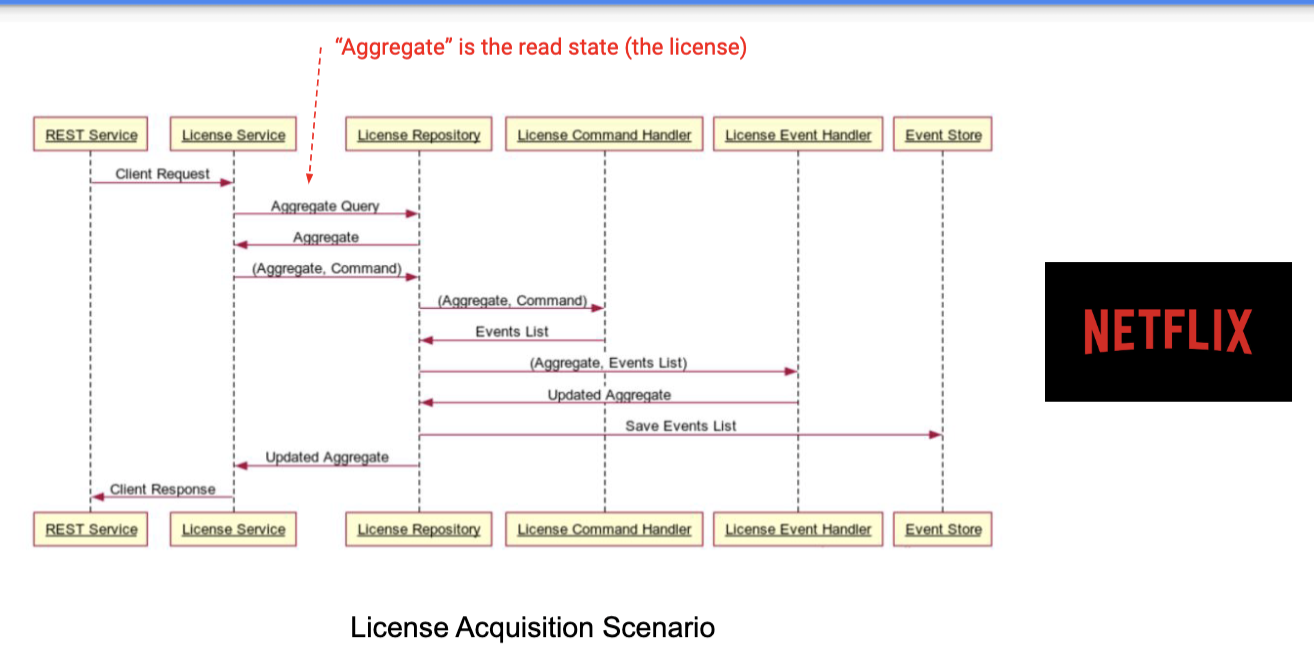
- pros: audit trail w. event trace -> allows for return to state with history, easy event replay without changing state
- cons: event structure changes -> end-to-end changes, must take snapshots of events, learning curve
CQRS + Event Sourcing 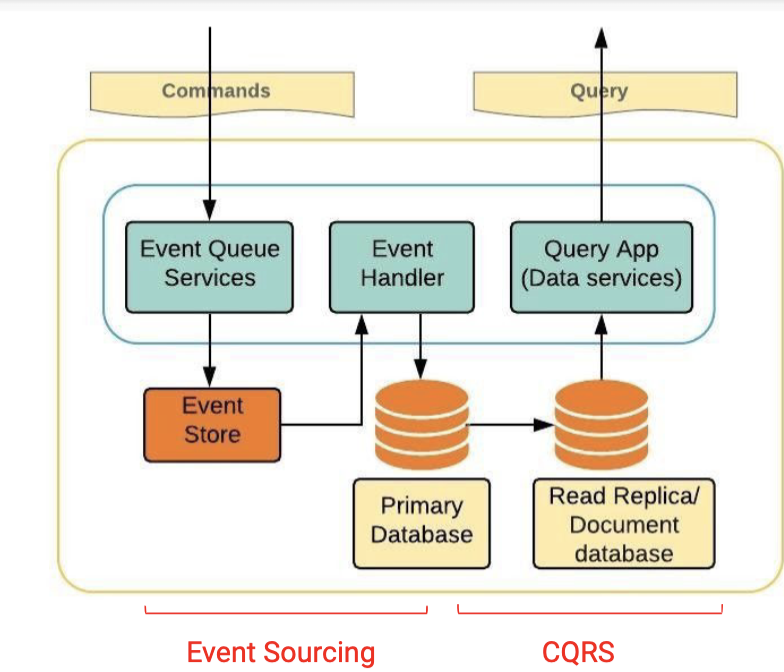
UI Patterns
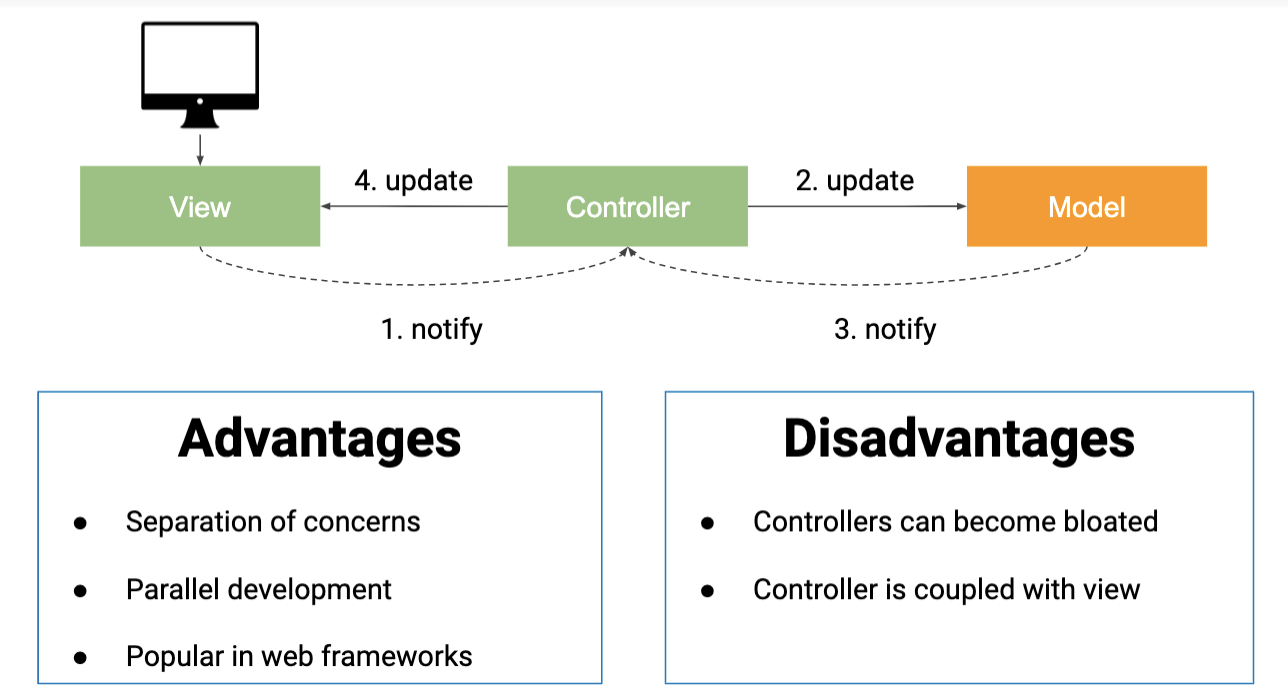
Model-View-Controller (MVC)
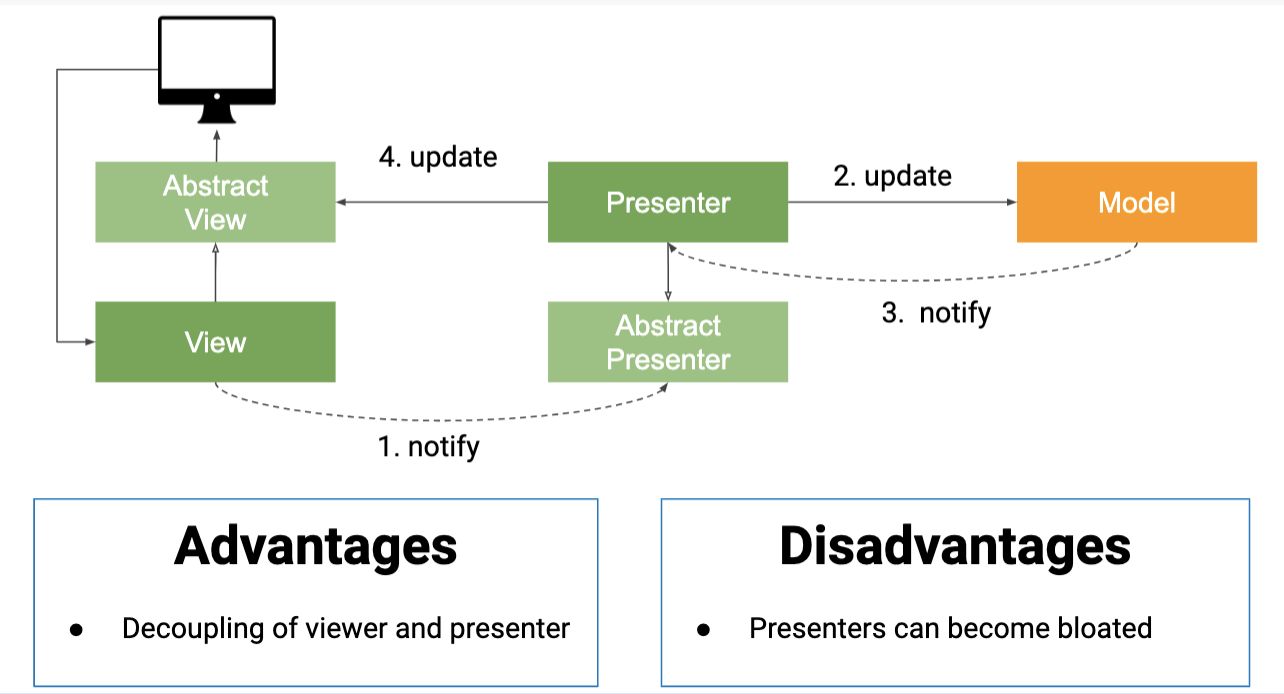
Model-View-Presenter (MVP)
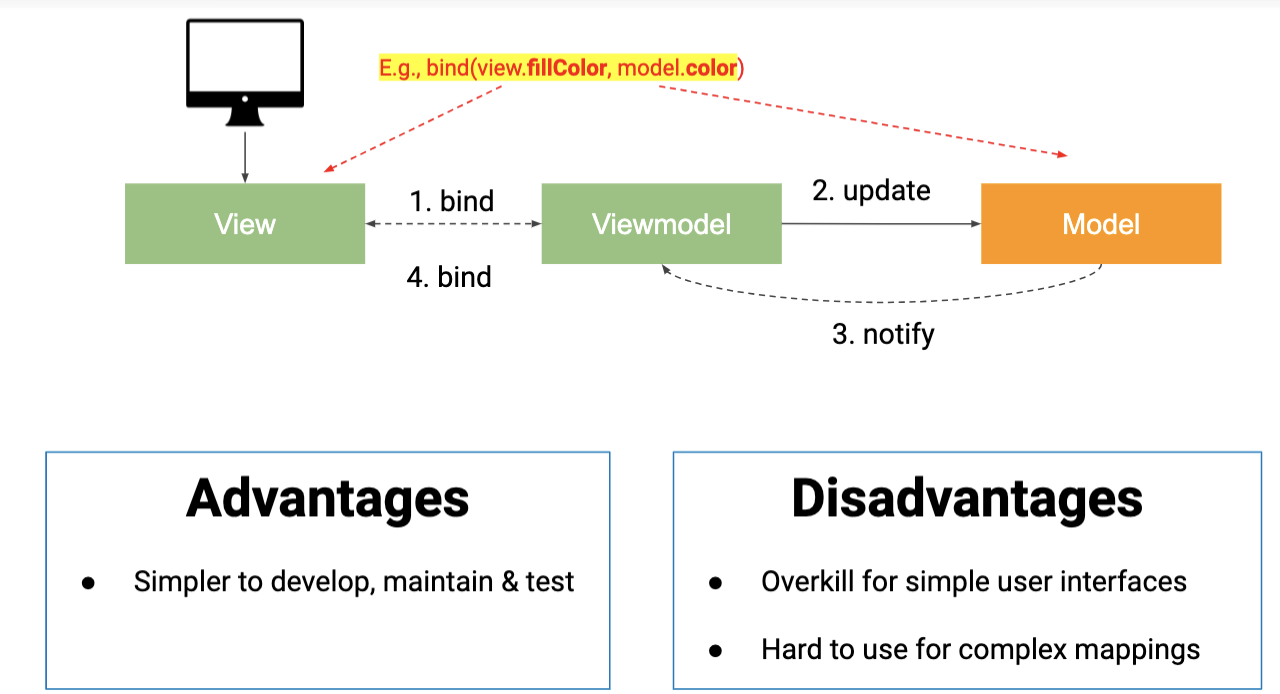
Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM)
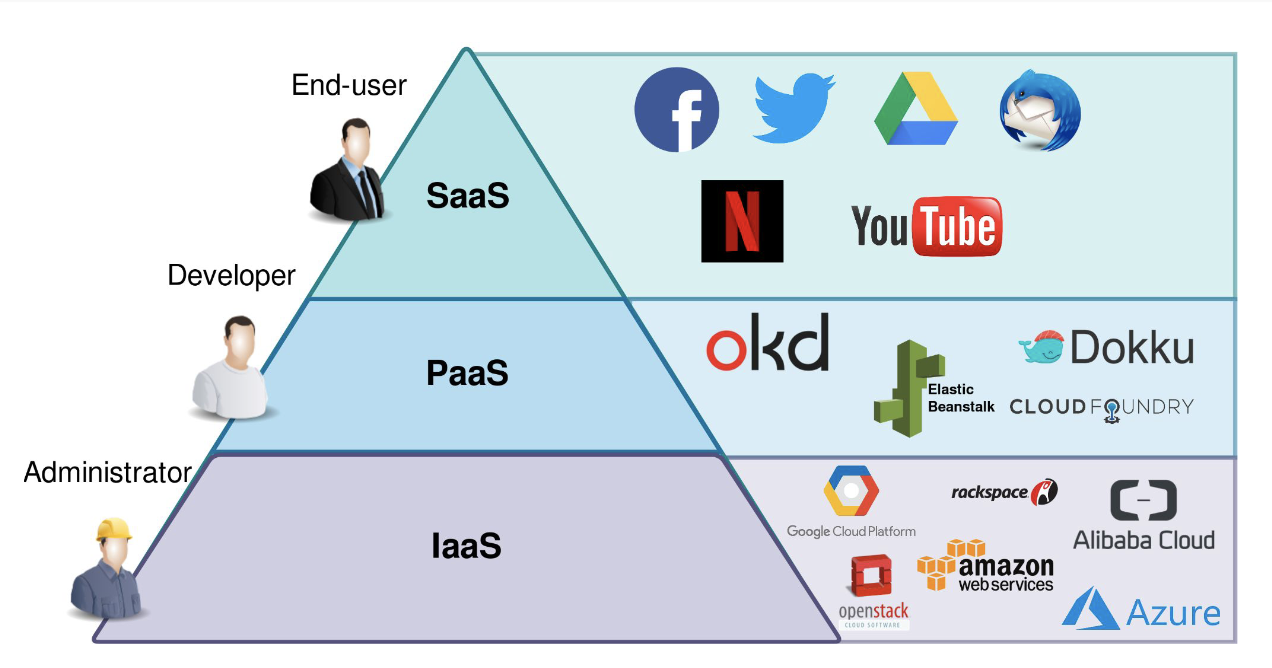
Cloud Based Architecture
- services (SaaS - Software as a service, PaaS - Platform…, IaaS - Infra…)
- scriptable infrastructure - infra as code for provisioning etc.
- improved dev lifecycle - no need to wait on hardware availability, just provision resources
- unconstrained resources - just provision more or switch compute to mitigate bottlenecks
- on-demand scaling - no compute bottleneck, just provision more
- high availability and disaster recovery - edge compute, load balancing, availability zones, etc. abstracted from developer
- shared security model - not all onus is on the dev to maintain security
- optimized cost - pay as you go, etc. allowing on demand products allows usage based on traffic and thus cost as busy